Introduction to Trademark Class 17
Trademark Class 17 represents a world of elasticity and adaptability, encompassing products made from rubber and similar materials that are utilized across various industries. It is vital in creating products that stretch, protect, and insulate, ranging from everyday necessities to industrial innovations.
This class encompasses a wide range of products such as Unprocessed and semi-processed rubber, gutta-percha, gum, asbestos, mica, and substitutes for all these materials; plastics and resins in extruded form for use in manufacture; packing, stopping, and insulating materials; flexible pipes, tubes, and hoses, not of metal.
It mainly includes electrical, thermal, and acoustic insulating materials and plastics for use in manufacture in the form of sheets, blocks, and rods, as well as certain goods made of rubber, gutta-percha, gum, asbestos, mica, or substitutes.
Let us discuss the products covered under Trademark Class 17 briefly:
a. Rubber and Gutta-Percha: This includes natural and synthetic rubbers, essential in manufacturing products that require elasticity and durability.
Example: RUBCO is an abbreviation for the Kerala State Rubber Co-operative Limited. This invention agency is tied up to the government of Kerala, and they acquire and process natural rubber from the farmers directly. This company supplies natural rubber directly to Indian companies and companies abroad too.
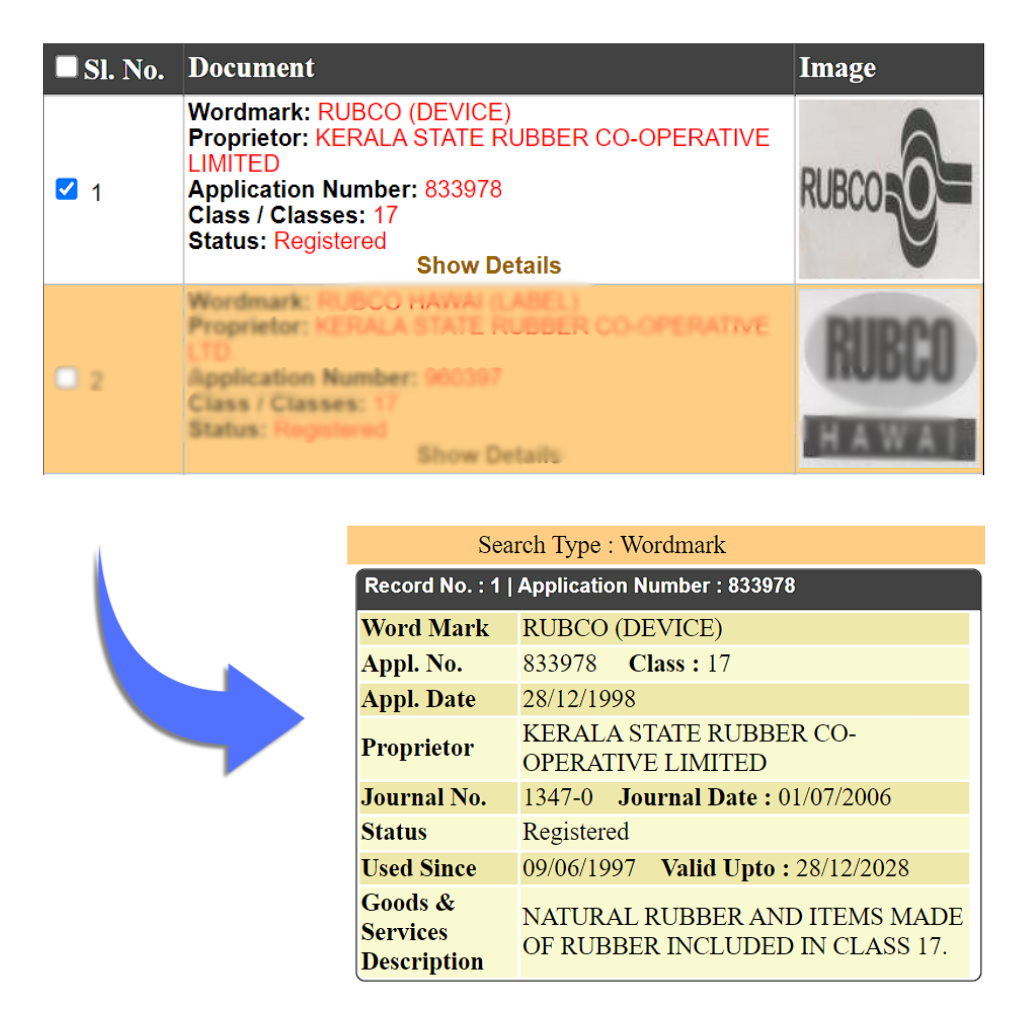
b. Rubber Sheets and Strips: This includes sheets and strips of rubber that serve as foundational materials for various applications,
Example: MRF Ltd. (Madras Rubber Factory) is one of India’s largest tyre manufacturers and is well-known for its extensive range of rubber products, including tires, tubes, and rubber compounds.
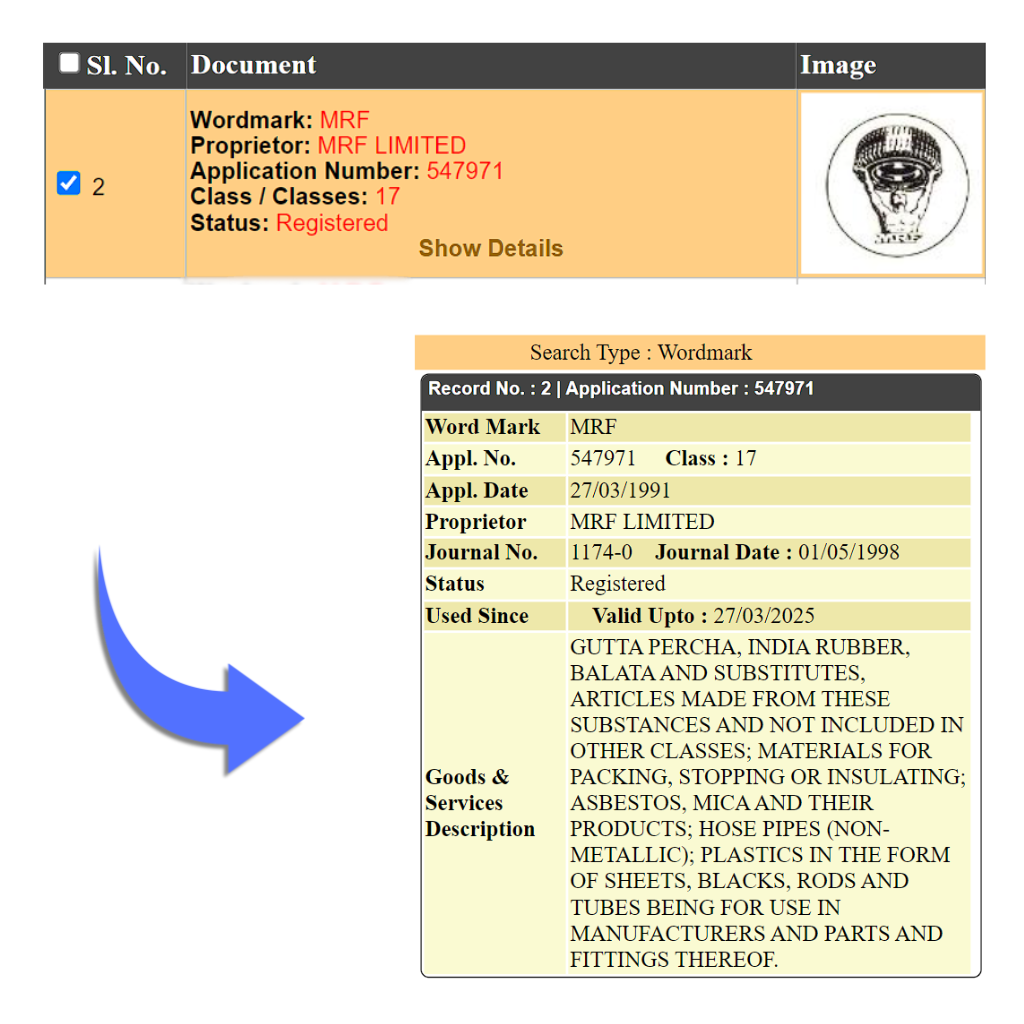
c. Rubber hoses and tubes: This includes hoses and tubes made from rubber, commonly used for conveying fluids and gases.
Example: Goodyear is renowned for its tires and rubber-based products covering a range of goods including tires, rubber hoses, etc
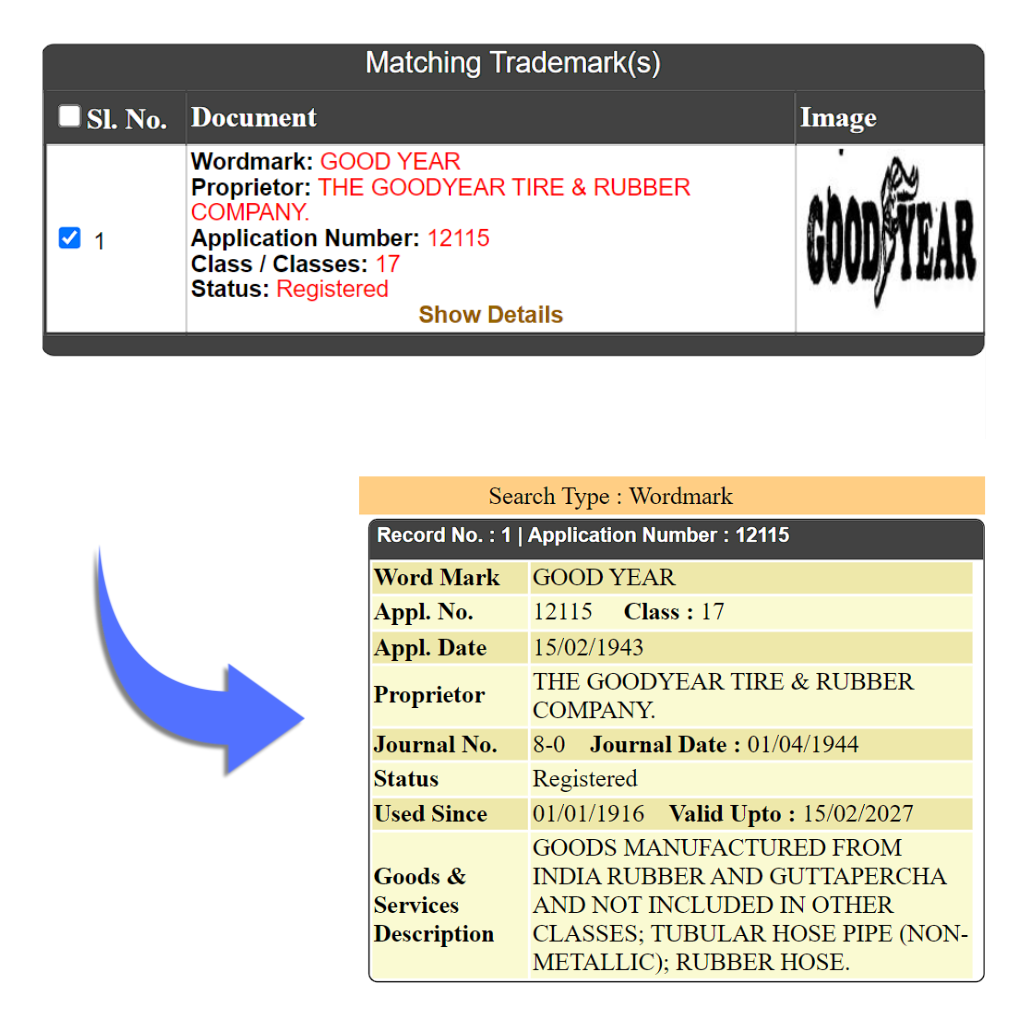
d. Rubber Seals and Gaskets: This covers rubber seals and gaskets that prevent leakage and provide insulation.
Example: Sealmax has emerged as trusted Gasket manufacturers in India.
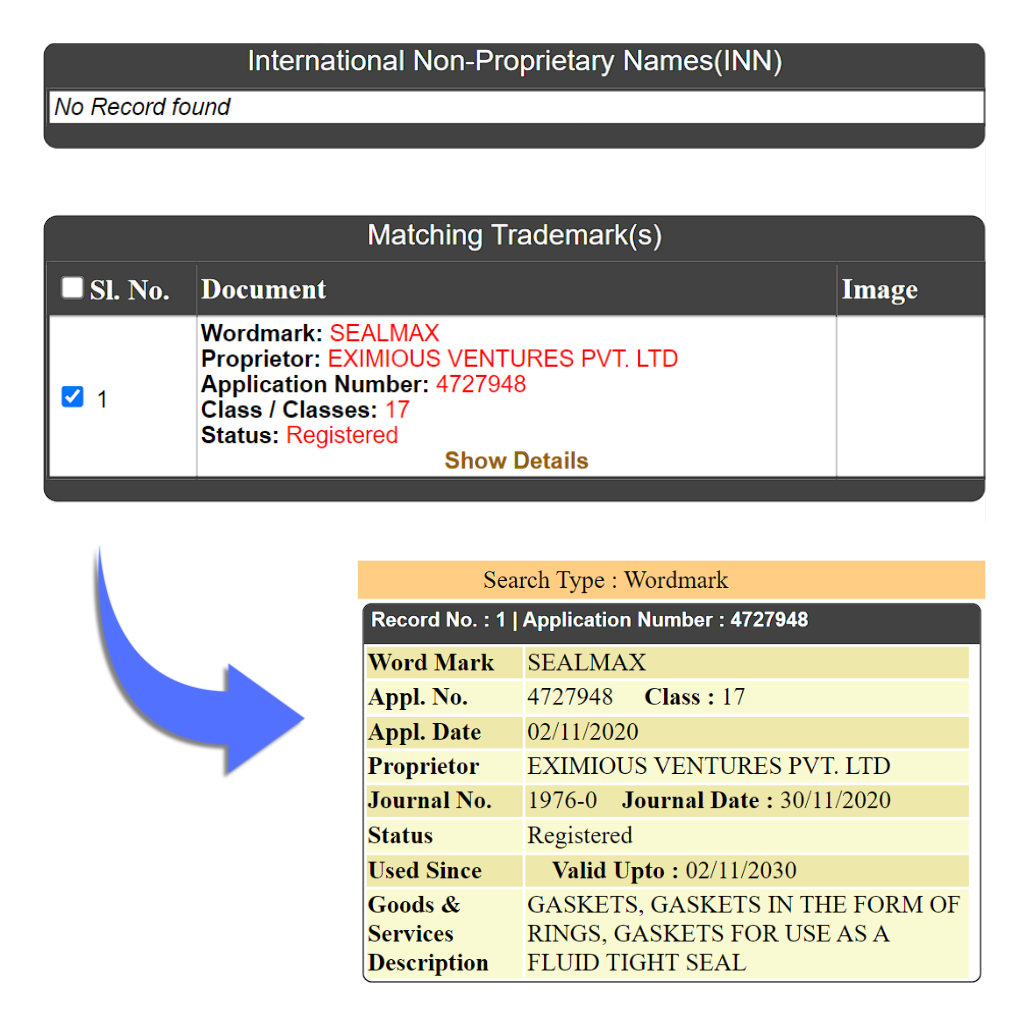
e. Insulating Materials: This includes Insulating materials for electricity, heat, and sound Rubber-based insulating materials, Insulating paints and coatings.
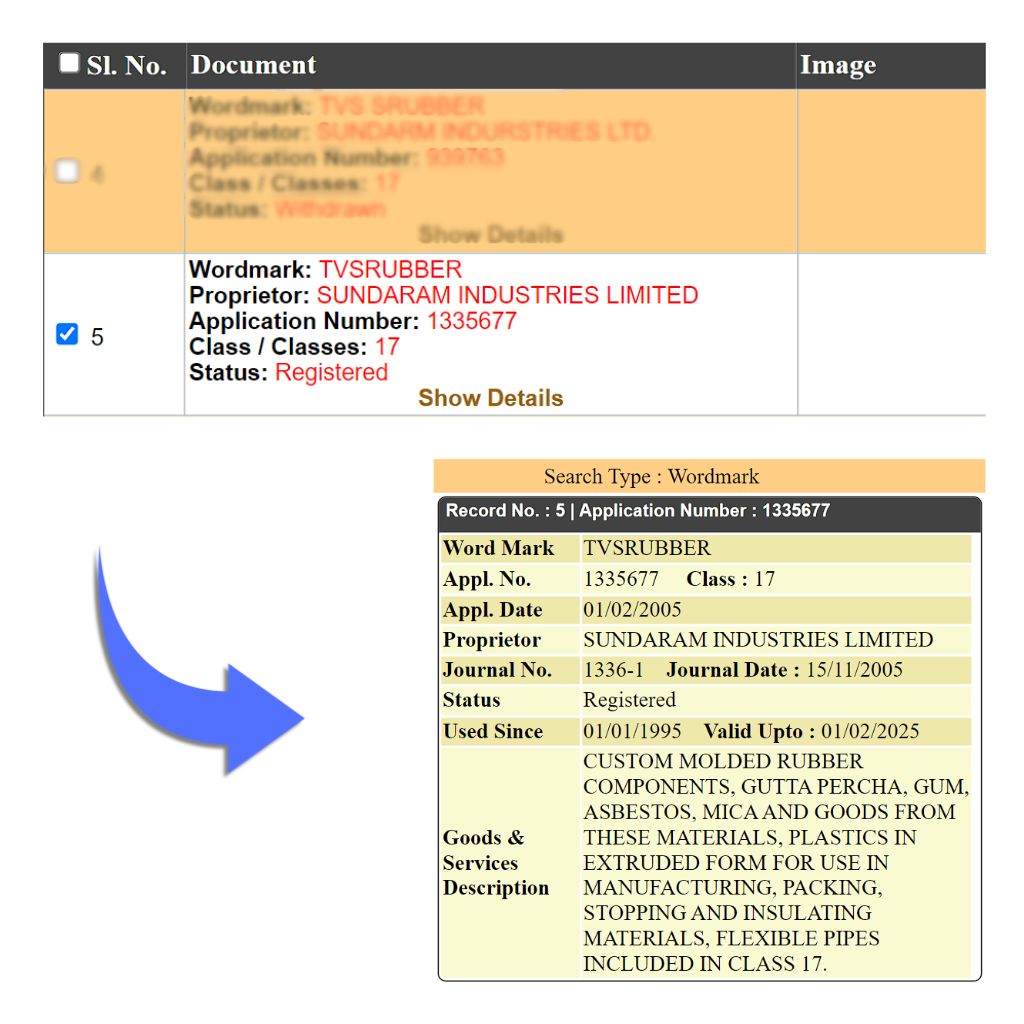
Example: TVS Rubber are leading Rubber compound developer and manufacturer of Rubber and polymer products used in various critical applications including Automotive, Railways, Defence, Mining, and Construction equipment.
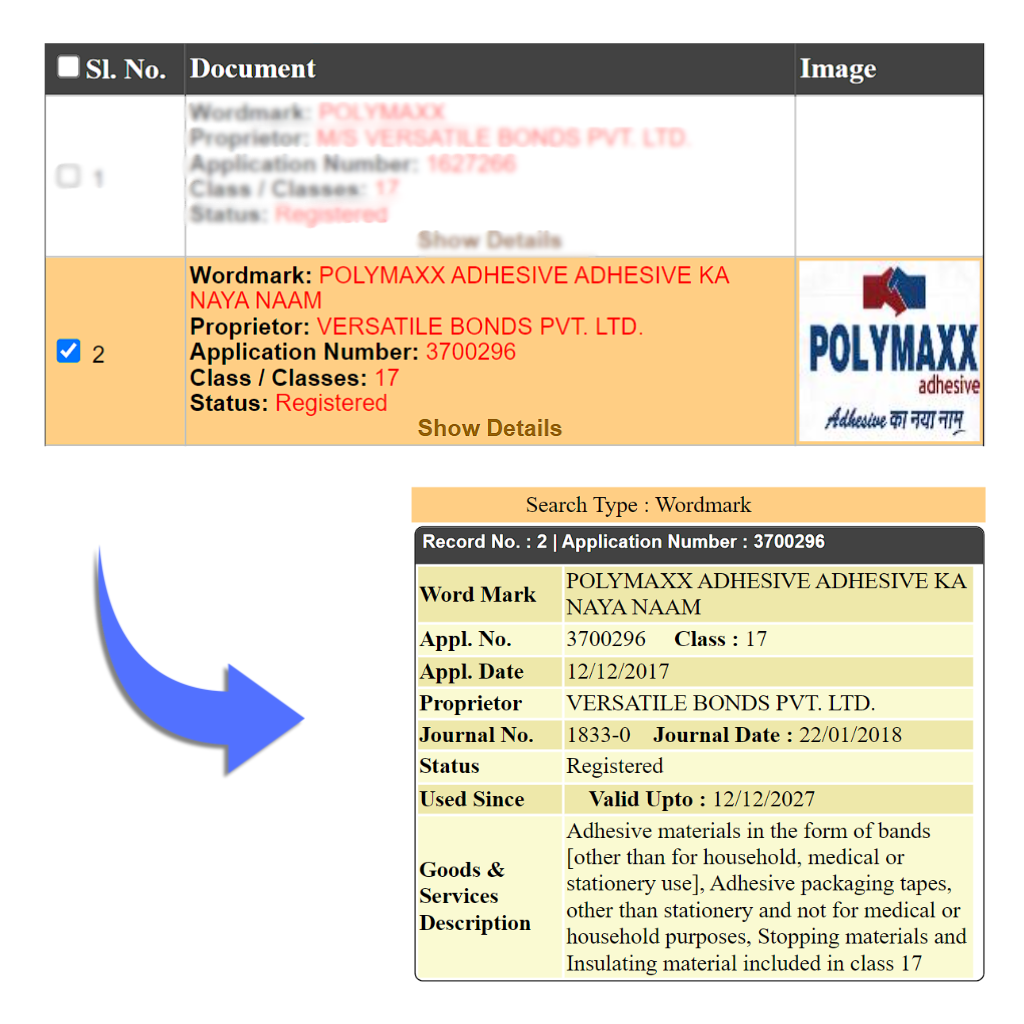
f. Adhesive Bands and Tapes: This includes Non-metallic adhesive tapes for industrial or commercial use and electrical insulating tapes.
Example: Polymax is a well-known company in India specializing in rubber and polymer products, including adhesive tapes.
Inclusions and Exclusions under Trademark Class 17
Trademark Class 17 covers a wide range of products as discussed above. Below is a detailed breakdown of the specific items included and excluded from this classification.
Specific Inclusions in Trademark Class 17:
✔ Rubber material for recapping tyres;
✔ Floating anti-pollution barriers;
✔ Adhesive tapes, other than stationery and not for medical or household purposes;
✔ Plastic films, other than for wrapping and packaging, for example, anti-dazzle films for windows;
✔ Elastic threads and threads of rubber or plastic, not for textile use;
✔ Certain goods made of the materials in this class are not otherwise classified by function or purpose, for example, foam supports for flower arrangements, padding and stuffing materials of rubber or plastics, rubber stoppers, shock-absorbing buffers of rubber, rubber bags or envelopes for packaging.
Specific Exclusions in Trademark Class 17:
✘ Fire hose (Class 9)
✘ Pipes being parts of sanitary installations (Class 11) and rigid pipes of metal (Class 6) and not of metal (Class 19).
✘ Insulating glass for building (Class 19).
✘ Certain goods made of the materials in this class are classified according to their function or purpose, for example, gum resins (Class 2), rubber for dental purposes (Class 5), asbestos screens for firemen (Class 9), adhesive rubber patches for repairing inner tubes (Class 12), erasers (Class 16).
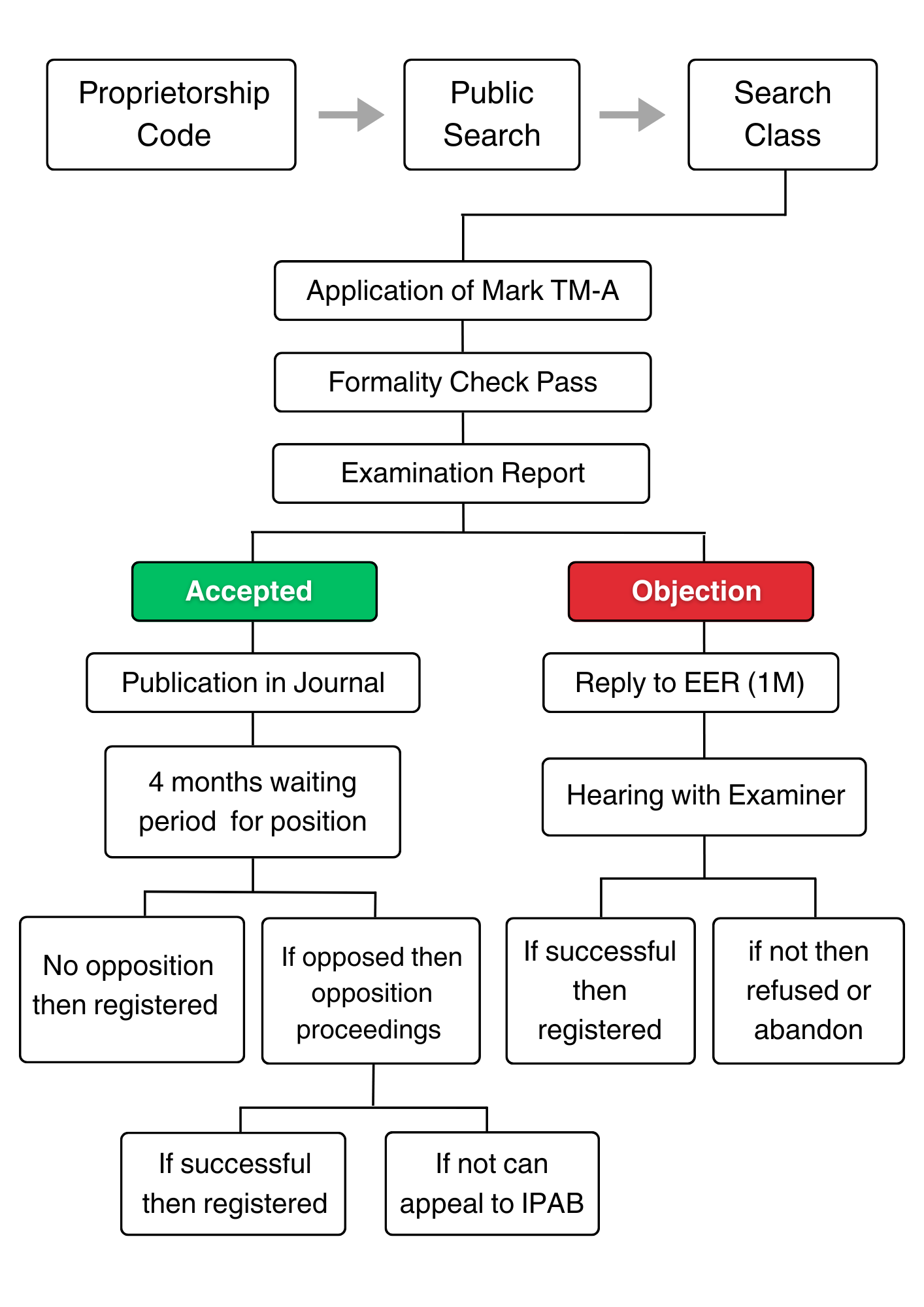
Steps involved in registering Trademark under Class 17
Initial Trademark Search for Trademark Class 17
Before starting with the registration process under Trademark Class 17, a detailed Trademark Search is required to be conducted to ensure that the proposed trademark is unique and does not conflict with existing trademarks under Trademark Class 17. Search can be carried out online through the official website of the Trademarks Registry (https://tmrsearch.ipindia.gov.in/tmrpublicsearch).
Prepare and Draft the Trademark Application for Trademark Class 17
For preparing and drafting the trademark application form (TM-A), the following information and documents are required to be collated:
- A clear representation of the trademark
- Details of the applicant, including name, address, and nationality
- Description of goods or services associated with the trademark
- Date of first use (if applicable)
- Power of Attorney (if filed through an attorney)
- Digital Signature of the Applicant
The application can be filed online through the official website or a physical application can be submitted at the nearest Trademarks Registry office.
Submit the Application for Trademark Class 17
The trademark application can be submitted online or offline by paying the requisite fees. The fee varies depending on whether you’re an individual, a startup, a small enterprise, or a large corporation.
Examination by the Trademarks Registry
The Trademarks Registry will review the application to ensure it complies with the relevant laws and regulations. They will assess the distinctiveness of the mark, potential conflicts, and other requirements.
Publication in the Trademarks Journal
If the Registrar finds no objections or issues with your application, your trademark will be published in the Trademarks Journal. This publication allows interested parties to oppose the registration within a specific period (usually four months).
Objection and Opposition Period
During the publication period, objections or oppositions can be filed by third parties against the proposed trademark. If an objection is filed, the opportunity to respond shall be granted.
Registration Certificate of Trademark Class 17
If there are no valid objections or if you successfully resolve any objections, the Registrar will issue a Certificate of Registration for trademark under Class 17. This certificate confirms your exclusive rights to the mark within Trademark Class 17.
Detailed List of goods classified under Trademark Class 17
A
|
B
|
C
|
D
|
E
|
F
|
G
|
H
|
I
|
J
|
L
|
M
|
N
|
O
|
P
|
R
|
S
|
T
|
V
|
W
|
Conclusion on Trademark Class 17
Trademark Class 17 encompasses a wide range of products made from rubber, as well as other flexible materials, that serve essential functions across various industries. etc. As technology evolves and innovation continues to reshape the world of rubber goods, proper classification and trademark protection under Class 17 are vital for establishing a brand’s dedication to quality, durability, and adaptability.
For businesses operating in the rubber goods industry, securing a trademark in Class 17 is essential to stand out in a competitive market and communicate its commitment to providing reliable sealing solutions. To explore other trademark classes, refer to the ” Trademark Class List 1 to 45 “.
Ensure your trademark is protected with expert assistance from Registration Arena. Contact us today to start the Trademark Registration process in India smoothly and efficiently.








