Setting up a new business involves a lot of considerations like what will be the scale of operations, how much paperwork will be required, what will be the business strategy, etc. Particularly for small and medium-scale operations, people usually need help to choose between sole proprietorship and partnership. In this blog, we will break down the major differences between sole proprietorship and partnership so that you can select the right form of business.
Before having a look at the difference between sole proprietorship and partnership, first, let us understand what is the meaning of sole proprietorship and partnership.
What is the Meaning of Sole Proprietorship?
A sole proprietorship is one of the oldest forms of business establishment. As the name suggests, ‘Sole’ means ‘Single’, and ‘Proprietorship’ means ‘Ownership’, sole proprietorship is a form of business organization in which there is a single owner. Therefore, a single person owns, manages, and controls the business. He is known as a ‘Sole trader’ or ‘Sole proprietor’.
Becoming a sole trader is relatively simple compared to other business structures. It enables a business to begin trading easily. Also, the requirements for record-keeping are far more straightforward than other business structures. For example, grocery shops, salons, freelancers, etc.
In addition, the owner enjoys all the benefits arising out of business such as profits, and also bears the risks of business. Moreover, events such as death and incapacity of the owner affect the continuity of the proprietorship firm.
Also Read: Advantages and Disadvantages of Sole Proprietorship
What is Partnership?
A ‘Partnership’ or ‘Partnership Firm’ is also a form of business organization. It is a type of legal entity in which two or more persons carry on a business together to earn profit. Individually, all of them are called ‘Partners’ and collectively ‘A firm’. Such partners shall enter into an agreement to govern their mutual rights and duties.
In addition, they share the risks and responsibilities of the business. Further, partners contribute capital for the functioning of the business and share the profits either equally or as per the agreement between them.
For example, Mr. A, a Chartered Accountant by profession, and Ms. B, a Company Secretary by profession, decide to enter into a partnership for providing consultancy services. They agree to share the profits of the business equally.
Read More: Advantages and Disadvantages of Partnership Firm
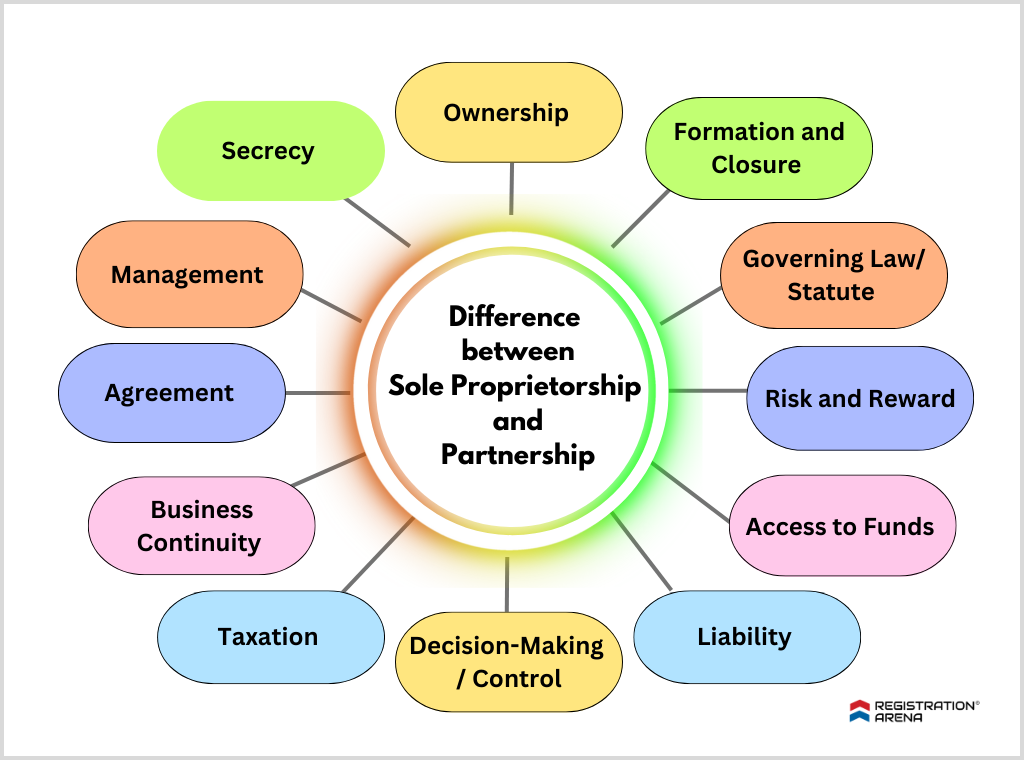
Difference between Sole Proprietorship and Partnership
Now that we know the meaning of sole proprietorship and partnership, let us understand the key difference between sole trader/ proprietorship and partnership.
The following are the main difference between sole proprietorship and partnership.
Ownership
In a sole proprietorship, there is a single owner. Therefore, the minimum and maximum number of owners in a sole proprietorship is 1.
While in partnership, the partners are like co-owners of the business. There shall be a minimum of two partners and the maximum number of partners in a partnership firm can be 50.
Formation and Closure
A sole proprietorship can be formed very easily with less paperwork. Also, as there is a single owner, it can be dissolved quickly without many formalities and processes.
To form a partnership firm, an agreement is necessary. In addition, if the partners decide to get the partnership firm registered, an application should be made to the Registrar of Firms. Moreover, the dissolution of a partnership firm also takes place in a formal manner and requires the consent of all the partners.
Therefore, the formation and closure of a partnership firm is more complex as compared to a sole proprietorship firm.
Governing Law/ Statute
There is no specific law that governs sole proprietorship in India.
On the other hand, the Partnership Act, of 1932 governs partnership firms in India.
Risk and Reward
In a sole proprietorship, there is no sharing of risk and reward. The sole owner enjoys all the benefits and bears the risk of the business.
While in partnership, the partners share the profits either in a predetermined ratio or equally. In addition, they bear the risk of the business together.
Credibility and Funding
A sole proprietorship business has access to limited funds only as the credibility of a sole proprietorship is generally low in the eyes of banks and other investors. Also, there are limited chances of expansion.
On the other hand, all the partners contribute capital to a partnership firm and it has higher credibility in the eyes of banks and other investors. Therefore, it is easier for partnership firms to raise funds.
Liability
In a sole proprietorship, the liability of the owner is unlimited. Therefore, in case of excessive losses, third parties can raise a claim against the personal assets of the owner like home, cars, personal bank account, etc.
While in partnership also, the liability of partners is unlimited but the difference is that they are jointly and severally liable for losses.
Therefore, just like profit, they share the losses as well. Also, there can be situations where one partner is held liable for the unlawful acts of the other partner(s).
Decision-Making/ Control
In a sole proprietorship, the owner takes all the decisions regarding the operation of the enterprise without having to seek the approval of any other person. Therefore, the decision-making process is flexible and changes can be implemented quickly.
On the other hand, in a partnership firm, partners take business decisions only after consultation with each other. There is a possibility that different partners have different opinions that can give rise to conflicts.
Therefore, the decision-making process is less flexible and more time-consuming in a partnership firm.
Taxation
The owner and the sole proprietorship firm are considered the same. The income from the sole proprietorship business is taxable in the hands of the owner as his business income. Therefore, one does not have to worry about paying taxes separately for the business.
Moreover, the income is taxed according to the slab system as applicable to individuals under the Income Tax Act, of 1961.
While a partnership firm is considered a separate legal entity from a taxation viewpoint, therefore, according to the provisions of the Income Tax Act, of 1961, a flat tax rate of 30% is applicable to the income of a partnership firm.
However, the partners’ share in such income is not taxable in the hands of such partners.
Business Continuity
The continuity of a sole proprietorship firm depends on the existence of the owner. With the death or incapacity of the owner, the sole proprietorship business also comes to an end.
On the other hand, in a partnership firm, events such as entry, exit, and death of partners lead to the dissolution of the partnership only and not the dissolution of the firm. Therefore, the firm can continue to operate.
Agreement
There is no need for an agreement as there is a single owner in a sole proprietorship.
While, in partnership, the partners shall enter into an agreement that governs their rights and duties. The agreement can be oral or in written form. When it is in writing, it is known as Partnership Deed.
However, it is always advisable to execute a written agreement to avoid conflicts or controversies in the future.
Management
The owner himself manages the sole proprietorship business. However, he can employ other individuals as well for carrying out different business operations such as purchase, sales, marketing, finance, etc.
On the other hand, all the partners manage the partnership firm together. In most cases, they divide the business management responsibilities amongst themselves.
Secrecy
In a sole proprietorship firm, it is easy to maintain secrecy as there is a single owner and he is not required to share the trade secrets with any other person.
While, in a partnership firm, it is difficult to maintain secrecy as the trade secrets are generally known to all the partners.
Registration of a Sole Proprietorship
Registration of sole proprietorship is not mandatory as it is not governed by any specific law in India. However, it can obtain local licenses and registration under state-specific laws such as the Shop Act Licence under the Shops and Establishment Act of the respective state.
Moreover, it can obtain Udyam (MSME) registration, GST registration, Trademark registration, etc. Please note that it becomes necessary to obtain GST registration if the aggregate turnover exceeds Rs. 10 lakhs in Special Category States and Rs. 20 lakhs in other states in case the person supplies both goods and services.
However, in case a person is engaged in the supply of taxable goods only, then GST registration is mandatory only if the aggregate turnover exceeds Rs. 40 lakhs.
Are you planning to obtain GST registration? Our experts can help you! Connect with us now.
Registration of a Partnership
The Partnership Act, of 1932 governs partnership firms in India. Accordingly, the registration of a partnership is not compulsory. However, if a partnership firm intends to obtain registration, it can make an application as per Section 58 of the Act.
Moreover, if a partnership firm is not registered, it suffers from several limitations. For example, it cannot file a suit against a third party for breach of contract.
Sole Proprietorship v/s Partnership: Which is Better?
The suitability of sole proprietorship and partnership as forms of business organization depends on several factors and varies from case to case.
A sole proprietorship is suitable for small-scale operations, individually managed occupations like salons, local market operations, etc. In addition, a sole proprietorship is ideal if you want to retain the entire control of the business in your hands.
On the other hand, a partnership firm is suitable for medium-sized businesses, providing services such as legal services, medical services, etc. Moreover, if two or more persons want to carry out business activities together by pooling their resources, it is better to select a partnership firm as a business structure.
Key Takeaway
There are many differences between sole proprietorship and partnership. Also, both forms of business organization have their own set of advantages and disadvantages. Therefore, one should be careful while making a choice between sole proprietorship and partnership and should select the form of business based on needs and suitability.