Introduction
India is encouraging the growth of startups by creating a supportive environment. A dedicated ministry is helping new businesses, and the government has launched Schemes for Innovative Startups to provide financial aid and assistance.
The Government introduced convertible notes for startups under the Companies Act, 2013. This term was first brought in by the Ministry of Corporate Affairs (MCA) through a notification on June 29, 2016. As per the amendment to Rule 2 of The Companies (Acceptance of Deposits) Rules, 2014, any amount of Rs 25 Lakhs or more received by a startup via convertible notes is exempted from being treated as a deposit.
Convertible notes are a common form of financing for start-up companies, providing flexibility for both the company and the investor. They allow the company to raise funds without immediately determining a valuation, and they offer investors the potential for equity ownership in the company at a later stage
What are Convertible Notes?
Companies Act 2013
A “convertible note” refers to a document confirming the receipt of funds initially as a debt. This debt is repayable at the discretion of the holder or can be converted into a specific number of equity shares of the startup company upon the occurrence of predetermined events. The terms and conditions governing this conversion are agreed upon and outlined in the instrument.
Foreign Exchange Management Act, 1999
A convertible Note means an instrument issued by a startup company acknowledging receipt of money initially as debt, repayable at the option of the holder, or which is convertible into such number of equity shares of that company, within a period not exceeding ten years from the date of issue of the convertible note, upon occurrence of specified events as per other terms and conditions agreed and indicated in the instrument.
Who is eligible to issue Convertible Notes?

Only a Start-Up Company, officially recognized by the Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT), is eligible to issue a Convertible Note. A “start-up” or “start-up company” refers to a private company incorporated under the Companies Act, 2013 recognized as a start-up by the Department of Industrial Policy and Promotion, Ministry of Commerce and Industry. (DIPP)
To qualify as a start-up according to the DPIIT notification dated February 19, 2019 (superseding the notification dated April 11, 2018), the entity must meet the following criteria:
- It must be a private company, limited liability partnership (LLP), or partnership firm. This includes a private company that serves as a subsidiary of a public company.
- The entity should not have been formed by dividing or reconstructing an existing business.
- It must be within 10 years from the date of its incorporation or registration.
- The turnover of the entity for any financial year since its incorporation or registration must not have exceeded Rs 100 Crores.
- The entity should be focused on the innovation, development, or improvement of products, processes, or services. Alternatively, it should have a scalable business model with a high potential for employment generation or wealth creation.
It’s important to note that an entity will cease to be considered a start-up upon completion of 10 years from the date of its incorporation or registration or if its turnover for any previous year exceeds one hundred crore rupees.
Conditions for issuing Convertible Notes
Under the Companies Act 2013-
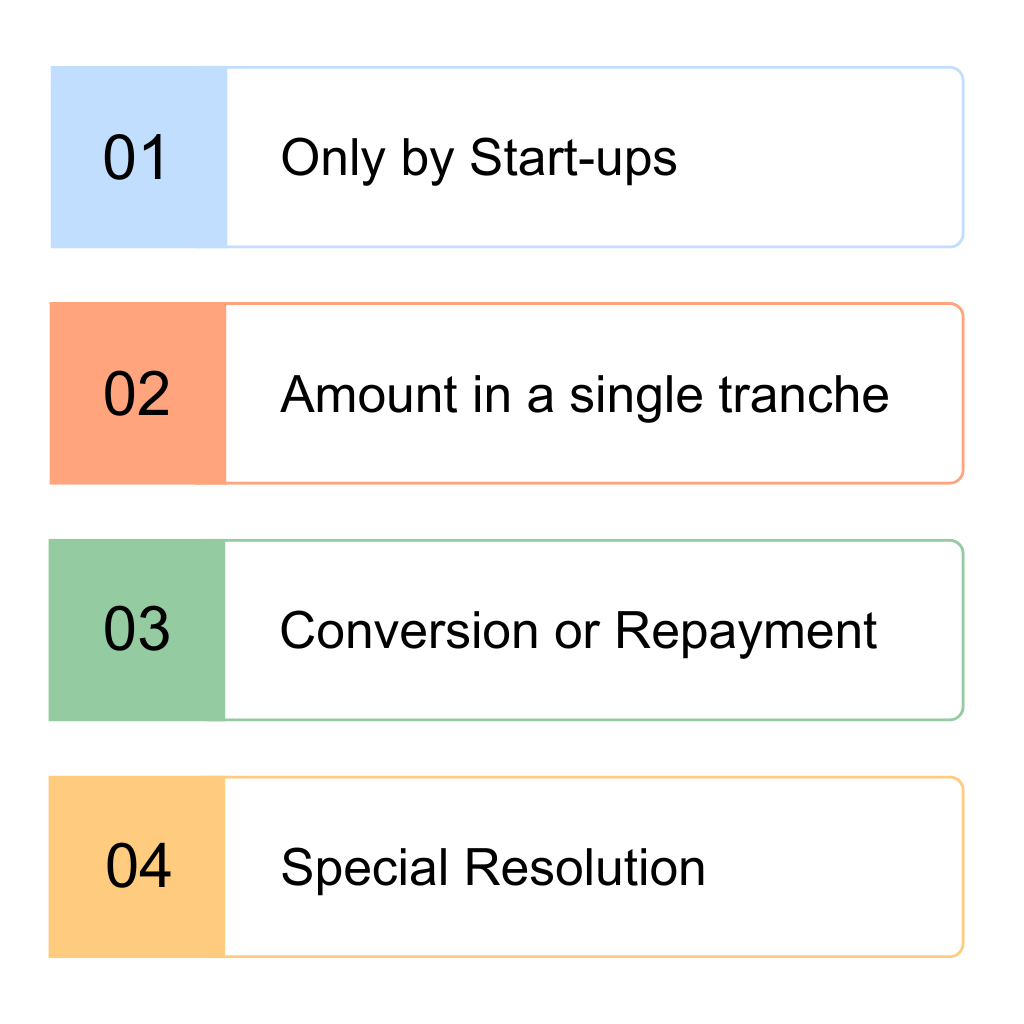
Only by Start-ups
Convertible notes can only be issued by startups registered with the Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade; otherwise, they will be categorized as deposits under section 73 of the Companies Act, 2013.
Amount in a single tranche
The issuance amount must be Rs 25,00,000 or more in a single tranche.
Conversion or Repayment
Convertible notes must be converted into equity or repaid within a 10-year period from the date of issue.
Special Resolution
According to Section 62(3) of the Companies Act, 2013, shareholder approval via Special Resolution is required for the issuance of convertible notes.
Under the Foreign Exchange Management Act, 1999
Foreign Exchange Management (Non-debt Instruments) Rules, 2019, and Foreign Exchange Management (Mode of Payment and Reporting of Non-Debt Instruments), Regulations, 2019
For issuing convertible notes, to a person resident outside India, the following conditions are required to be complied under FEMA Laws:
Eligibility for Foreign Investors
Foreign investors, excluding individuals from Pakistan or Bangladesh or entities registered in Pakistan or Bangladesh, can purchase convertible notes issued by Indian start-up companies for amount equal to or greater than Rs 25,00,000 in a single tranche.
Sectoral Restrictions
Start-up companies operating in sectors requiring government approval for foreign investment must obtain such approval before issuing convertible notes to foreign investors. Additionally, any conversion of these notes into equity shares must comply with foreign investment regulations regarding entry routes, sectoral caps, and pricing.
Mode of Payment and Remittance Conditions
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) specifies the mode of payment and other conditions for remitting sale proceeds or maturity proceeds related to convertible notes.
Non-Repatriation Basis for NRIs and OCIs
Non-resident Indians (NRIs) and Overseas Citizens of India (OCIs) have the option to acquire convertible notes on a non-repatriation basis. This means that the investment made by NRIs or OCIs in convertible notes cannot be repatriated (transferred back) to their home country. Instead, the investment remains within India as per the regulations outlined in Schedule IV of the rules governing foreign investment in convertible notes.
Transfer of Convertible Notes
A person resident outside India may acquire or transfer by way of sale, convertible notes, from or to, a person resident in or outside India, However, such transfers must adhere to the entry routes and pricing guidelines prescribed for capital instruments.
Receipt of Consideration
When a startup company issues convertible notes to a non-resident individual or entity, it must receive the consideration amount either through inward remittance via banking channels or by debiting the NRE/FCNR(B)/Escrow account maintained by the concerned person, as per the Foreign Exchange Management(Deposit) Regulations, 2016.
Advantages of Convertible Notes

Flexibility
Convertible notes allow start-ups to raise capital without immediately determining a valuation. This flexibility is particularly beneficial for early-stage companies that may have uncertain valuations.
Less Ownership Dilution
Convertible notes start as debt, so they delay the dilution of ownership for existing shareholders compared to issuing equity directly. This can be advantageous for founders and early investors.
Easy Terms
Convertible notes often have simpler terms compared to equity financing rounds, which can streamline the fundraising process and reduce legal costs.
Postponed Valuation
Start-ups can wait to determine their value until a later stage, avoiding disagreements about worth early on.
Attractiveness to Investors
Convertible notes offer investors the potential for equity upside in the future while providing downside protection through the repayment option. This can make them attractive to angel investors and venture capitalists.
Establish Relationships
Issuing convertible notes can help start-ups establish relationships with potential future investors, as they may convert their notes into equity in subsequent financing rounds.
Boost Growth
Money from convertible notes can be used to grow the business faster, like improving products, advertising, and hiring more staff.
Disadvantages of Convertible Notes
Interest Payments
Unlike equity financing, convertible notes require the start-up to pay interest to investors until the notes convert into equity. This adds to the financial burden, especially if the company is not yet profitable.
Uncertain Conversion
The conversion of convertible notes into equity depends on future events, such as a subsequent financing round or acquisition. If these events don’t occur or if the valuation is unfavorable, it can lead to disagreements between the company and investors.
Potential Debt Burden
If the start-up fails to raise additional capital or achieve significant growth within the conversion period, it may have to repay the principal amount of the convertible notes. This can strain the company’s finances, especially if it’s struggling.
Ownership Dilution
While convertible notes delay immediate dilution of ownership, they can lead to significant dilution when they convert into equity, especially if the company raises subsequent rounds of financing at higher valuations.
Complex Terms
Negotiating the terms of convertible notes, such as the conversion discount, valuation cap, and interest rate, can be complex and time-consuming. Disagreements over these terms can strain relationships between the company and investors.
Limited Say for Investors
Investors with convertible notes usually can’t influence company decisions much compared to those who own shares. They have less control.
Legal Risks
If the terms of convertible notes aren’t clear, it can lead to fights between the company and investors, costing time and money and harming the company’s reputation.
Procedure under the Companies Act, 2013
For issue of Convertible Notes –
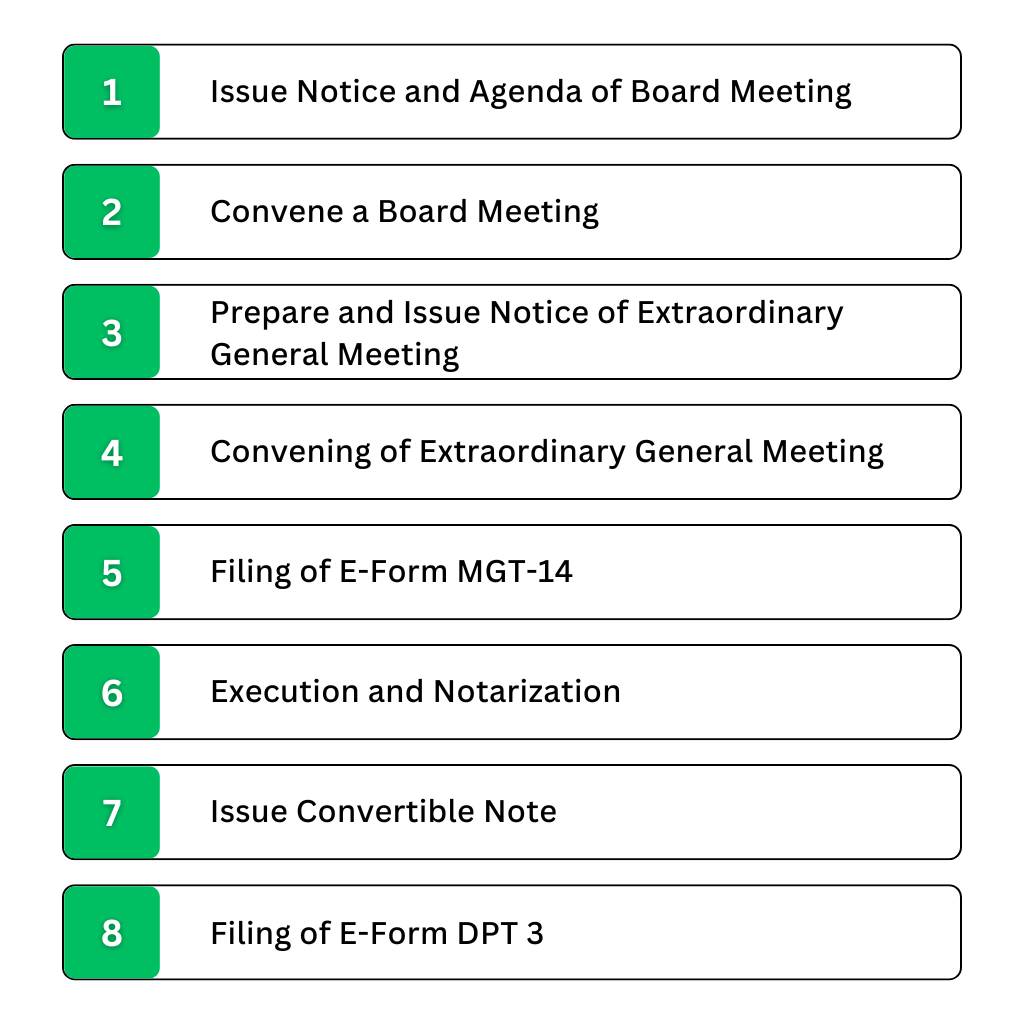
Issue Notice and Agenda of Board Meeting
Prepare and issue notice calling Board Meeting to all the directors at least seven days before the date of the Meeting by hand or by speed post or by registered post or by facsimile or by e-mail or by any other electronic means.
Convene a Board Meeting
Conduct a Board Meeting and pass Board Resolution for approving the issue of convertible notes and terms and conditions of the draft convertible note agreement and fix the day, date, place and time of Extraordinary General Meeting of the members for obtaining consent by way of Special Resolution.
- Prepare and Issue Notice of Extraordinary General Meeting :
Prepare and issue a notice in writing calling an Extraordinary General Meeting by giving at least 21 days clear notice to all the members by hand or by ordinary post or by speed post or by registered post or by courier or by facsimile or by e-mail or by any other electronic means. An explanatory statement must be annexed with the Notice of the meeting.
Convening of Extraordinary General Meeting
Convene an extraordinary general meeting and pass a Special Resolution for approving the issue of convertible notes and terms and conditions of the convertible note agreement and authorize any person to execute the Convertible Note Agreement on behalf of the Company.
Filing of E-Form MGT-14
File e-form MGT-14 with Registrar of the Company within 30 days from passing of Special Resolution.
Execution and Notarization
The convertible note agreement must be executed by the authorized person on behalf of the company and the investors. It must also be notarized.
Issue Convertible Notes
Issue the convertible notes to the investors upon receipt of the agreed investment amount.
Filing of E-Form DPT 3
An amount of Rs. 25 lacs or more received by a Start-up Company by way of Convertible Note is treated as an exempted deposit. Every company shall on or before the 30th day of June, of every year, file with the Registrar, a return in E-Form DPT-3 for reporting the exempted deposits.
Conversion of Convertible Notes
The company has the option to convert the convertible note into equity shares either upon the completion of 10 years or when specific events outlined in the convertible note agreement occur, whichever happens earlier. This conversion is conducted at the predetermined conversion price agreed upon in the terms and conditions of the convertible note.
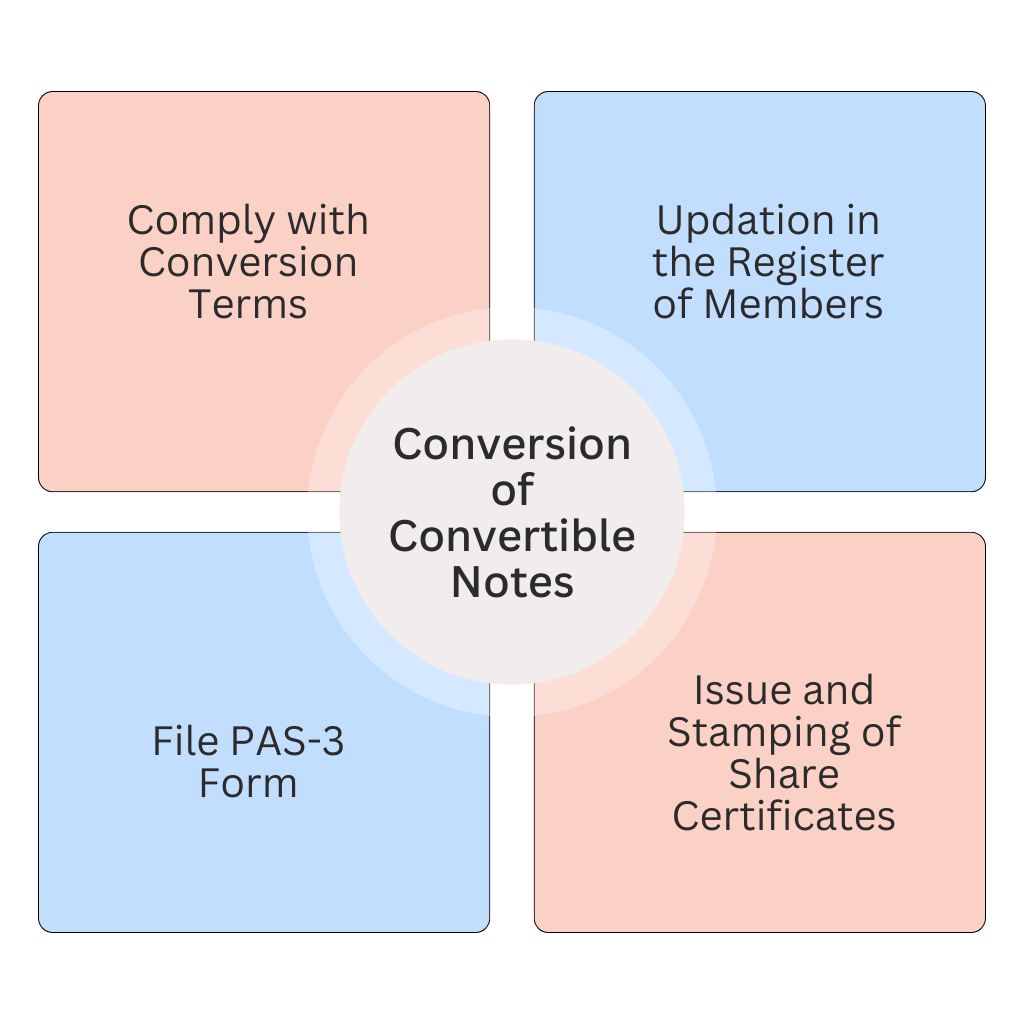
1. Comply with Conversion Terms
Ensure compliance with the terms and conditions of conversion as specified in the convertible note agreement. This includes the conversion price, timing, and any other relevant provisions.
2. File PAS-3 Form
Within 30 days of the allotment of equity shares upon conversion, the company must file Form PAS-3 with the Registrar of Companies (RoC). This form notifies the ROC about the allotment of shares and includes details such as the number of shares allotted, the consideration received, and other relevant information.
3. Issue and Stamping of Share Certificates
Issue Share Certificates within a period of 2 months from the date of allotment and stamp the share certificates within 30 days from the date of issuance of share certificates.
4. Updation in the Register of Members
Make necessary entries in the register of members by including the details of the shareholder such as name, address, number of shares, folio no, date of issue, etc.
Reporting Requirements under FEMA
- Create entity master account and business user registration on the FIRMS Portal.
- Indian startup companies issuing convertible notes to non-residents must file Form CN within 30 days of the issuance of such notes.
- A person resident in India, who may be a transferor or transferee of convertible notes issued by an Indian start-up company shall report such transfers to or from a person resident outside India, as the case may be, in Form CN within 30 days of such transfer.
- Indian companies that have received Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) are required to submit Form FLA to the Reserve Bank of India on or before the 15th day of July each year.
- The pricing or conversion formula of the instrument must be determined upfront at the time of its issuance. The conversion price should not be lower than the fair value calculated at the time of issuance in accordance with FEMA regulations.
- For reporting Convertible Notes issuance, documents required are:
- Foreign Inward Remittance Certificate (FIRC) or Debit advice
- KYC of the non-resident investor,
- Details of the investor and authorized dealer bank
- Declaration and Company Secretary Certificate,
- MOA/AOA,
- Certificate of Incorporation
- Start-up Registration Certificate,
- PAN of the Company, and
- Valuation Report issued by SEBI registered Merchant Banker/Chartered Accountant/Cost Accountant.
- Upon conversion of Convertible Notes to Equity Shares, Form FC GPR must be filed within 30 days from the date of allotment of equity shares resulting from the conversion.
Tax Implications
- There are no specific provisions in the Income Tax Act, 1961 that provide tax exemption for convertible notes issued by start-up companies. However, the tax treatment of convertible notes may depend on various factors, including whether they are treated as debt or equity, the terms of conversion, and the purpose of the investment.
- Typically, interest paid on convertible notes is treated as an expense and deductible for the issuing company, while the conversion of notes into equity shares may have tax implications for both the company and the note holder.
- Any gains or losses resulting from the conversion or sale of equity shares acquired through convertible notes may also be subject to taxation under the capital gains tax provisions. If the conversion price exceeds the fair market value, the company might face taxation under section 56 (2) (viib) of the Income Tax Act, 1961. Conversely, if the conversion price is lower than the fair market value, the holder of the convertible note could face taxation under section 56 (2) (x) of the Income Tax Act, 1961.
Applicable Forms and Fees
E-Form MGT-14
Form MGT–14 is to required be filed with a certified true copy of the special resolution passed at the general meeting and the explanatory statement annexed to the notice of the general meeting The Government (ROC) Fees for filing E-Form MGT-14 with the Registrar are as follows:
| Nominal Share Capital | Fees Applicable (Rs) |
| Less than 1,00,000 | 200 |
| 1,00,000 to 4,99,999 | 300 |
| 5,00,000 to 24,99,999 | 400 |
| 25,00,000 to 99,99,999 | 500 |
| 1,00,00,000 or more | 600 |
A fixed fee of Rupees (INR) 200 to be charged in case the company does not have share capital.
E-Form PAS 3
E-Form PAS 3 is required for filing a Return of allotment application by the company to the Registrar of Companies (RoC) post allotment of shares. The Government (ROC) Fees for filing E-Form PAS-3 with the Registrar are as follows:
| Nominal Share Capital | Fees Applicable (Rs) |
| Less than 1,00,000 | 200 |
| 1,00,000 to 4,99,999 | 300 |
| 5,00,000 to 24,99,999 | 400 |
| 25,00,000 to 99,99,999 | 500 |
| 1,00,00,000 or more | 600 |
A fixed fee of Rupees (INR) 200 is to be charged in case the company is not having a share capital.
E-Form DPT 3
A company other than a government company is required to file webform DPT-3 with the Registrar, in respect of particulars of transactions not considered as deposits on or before the 30th day of June, of every year. The government (ROC) Fees for filing E-Form PAS-3 with the Registrar are as follows:
| Nominal Share Capital | Fees Applicable (Rs) |
| Less than 1,00,000 | 200 |
| 1,00,000 to 4,99,999 | 300 |
| 5,00,000 to 24,99,999 | 400 |
| 25,00,000 to 99,99,999 | 500 |
| 1,00,00,000 or more | 600 |
A fixed fee of Rupees (INR) 200 is to be charged in case the company is not having a share capital.
Conclusion
In simple terms, convertible notes are a way for start-up companies to borrow money from investors with the promise of repaying them later or converting the loan into company ownership (equity) at a future date. For investors, this means they can potentially become shareholders in the company if it does well.
However, there are risks involved, like uncertainty about when and how much their investment will convert into equity. Therefore, it’s crucial for both start-ups and investors to carefully negotiate and document the terms of convertible notes and seek professional advice from our experienced team at Registration Arena to ensure compliance with regulatory requirements and mitigate potential risks.
Get in touch with us to learn more about how convertible notes can fuel your company’s growth and innovation.








