Introduction to Types of Trademark
A trademark (popularly known as a brand name in layman’s language) is any sign that individualizes the goods of a given enterprise and distinguishes them from the goods of its competitors. A Trademark is a type of Intellectual Property that can typically be “Name”, “Word”, “Phrase”, “Logo”, “Symbol”, “Design”, “Image” or a combination of all these elements. The origin of trademark dates back to ancient times when artisans marked their products to signify ownership and quality.
Over the years, this practice has evolved into a formal system of Trademark Registration and protection, which helps consumers identify and select products based on their quality and reputation. Trademark is a product of competitive trade practices. Every trader seeks to sell his product by its name and distinctiveness. The changing business practices have also changed the concept and philosophy of Trademark. It is, therefore, necessary to understand the different types of trademark.
In this blog let us discuss various types of trademark, important points to be noted, how to register trademark in India, etc.

Types of Trademark with Examples
Product Mark
A product mark is a type of trademark that is used specifically for products or goods, but not on services. It is used to identify the provider, the reputation, and the origin of the product. Applications for a trademark filed under Class 1-34 The Fourth Schedule To Trade Marks Rules, 2002 are generally termed as product marks. It is a product mark attached to goods for the purpose of indicating their origin. It also represents the distinctiveness and goodwill of a business from that of others. E.g. Parle-G, Colgate
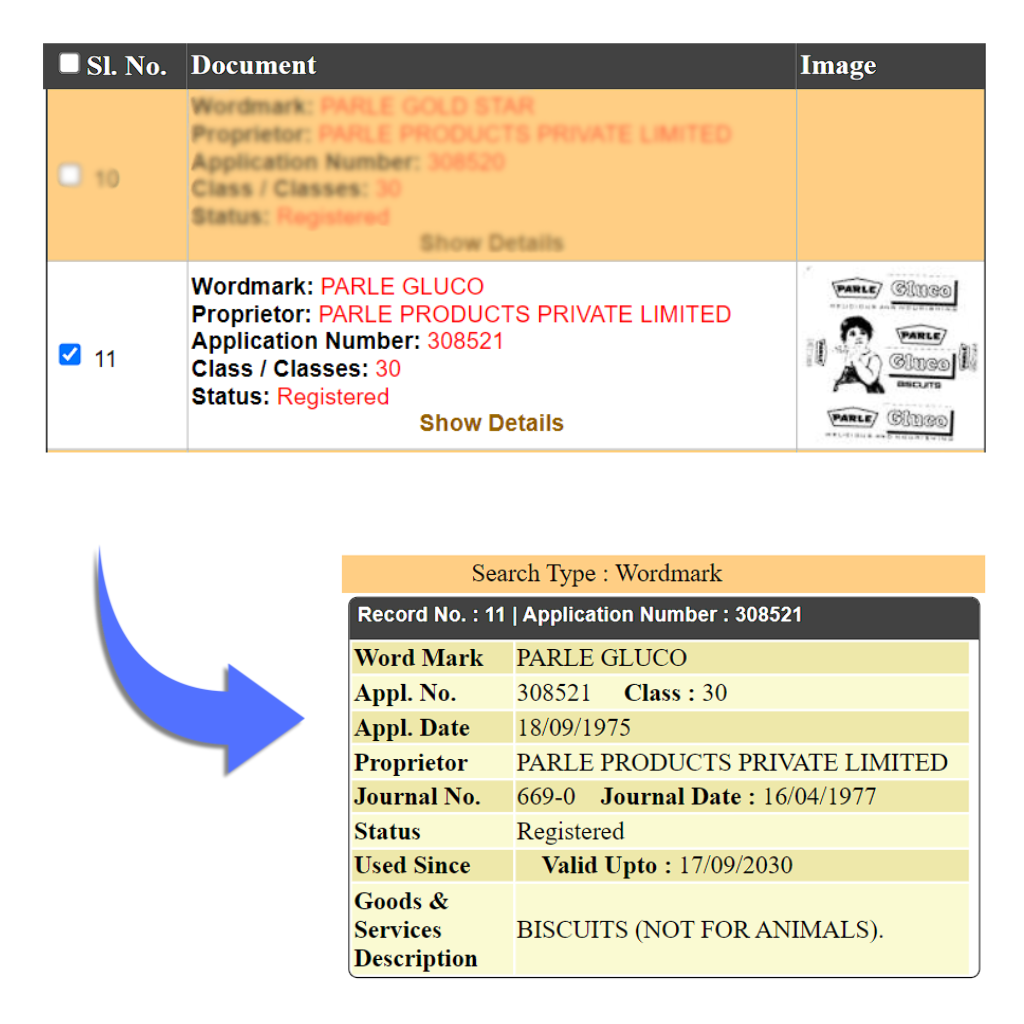
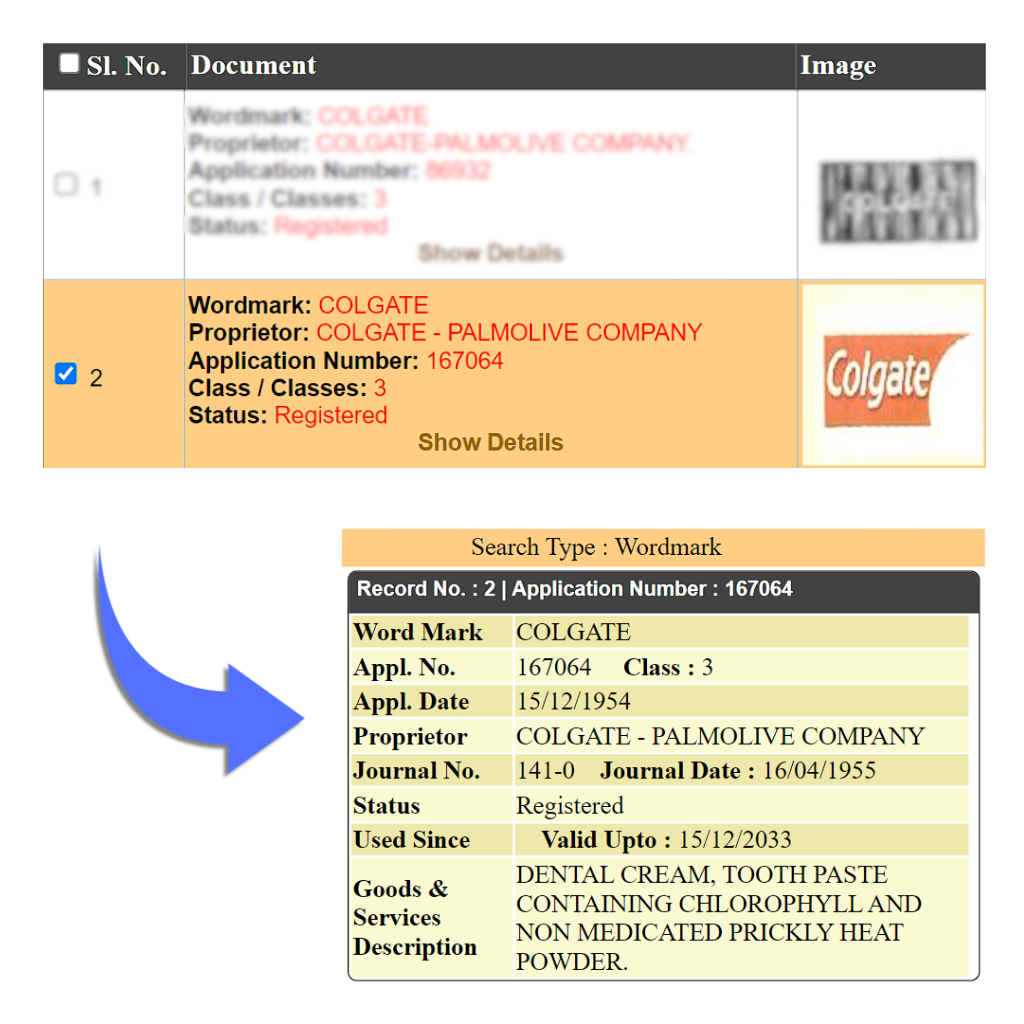
Word Mark
A Word Mark is a type of trademark that consists of words, letters, numerals, or any combination of these. It is used to identify the products and services of a company. In a Word Mark registration, attention is not given to the style or manner in which the words or letters are written, represented, the font size used, the design attached with the words, or any other graphic feature of the letters or words. Word Mark is used when your product is text-based or only letter-based or just your business name. E.g. Reliance, TATA
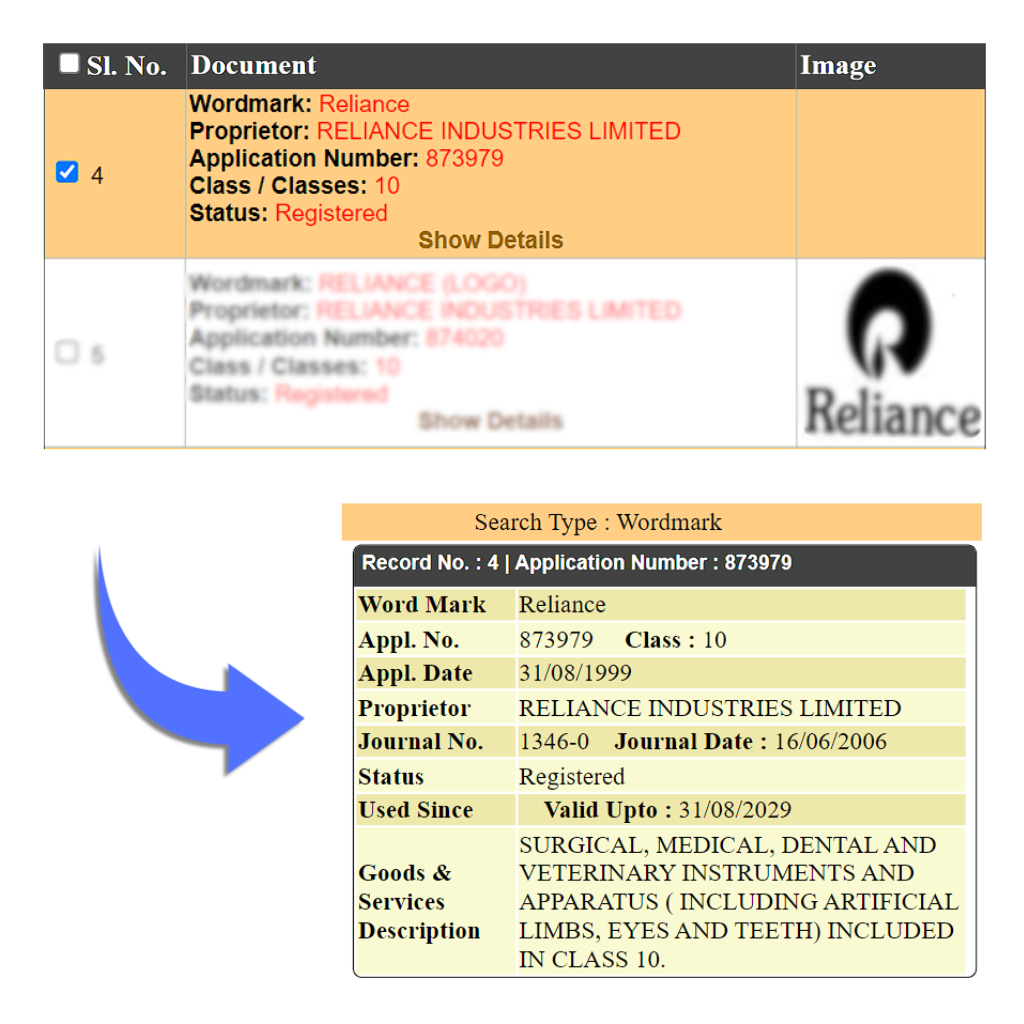
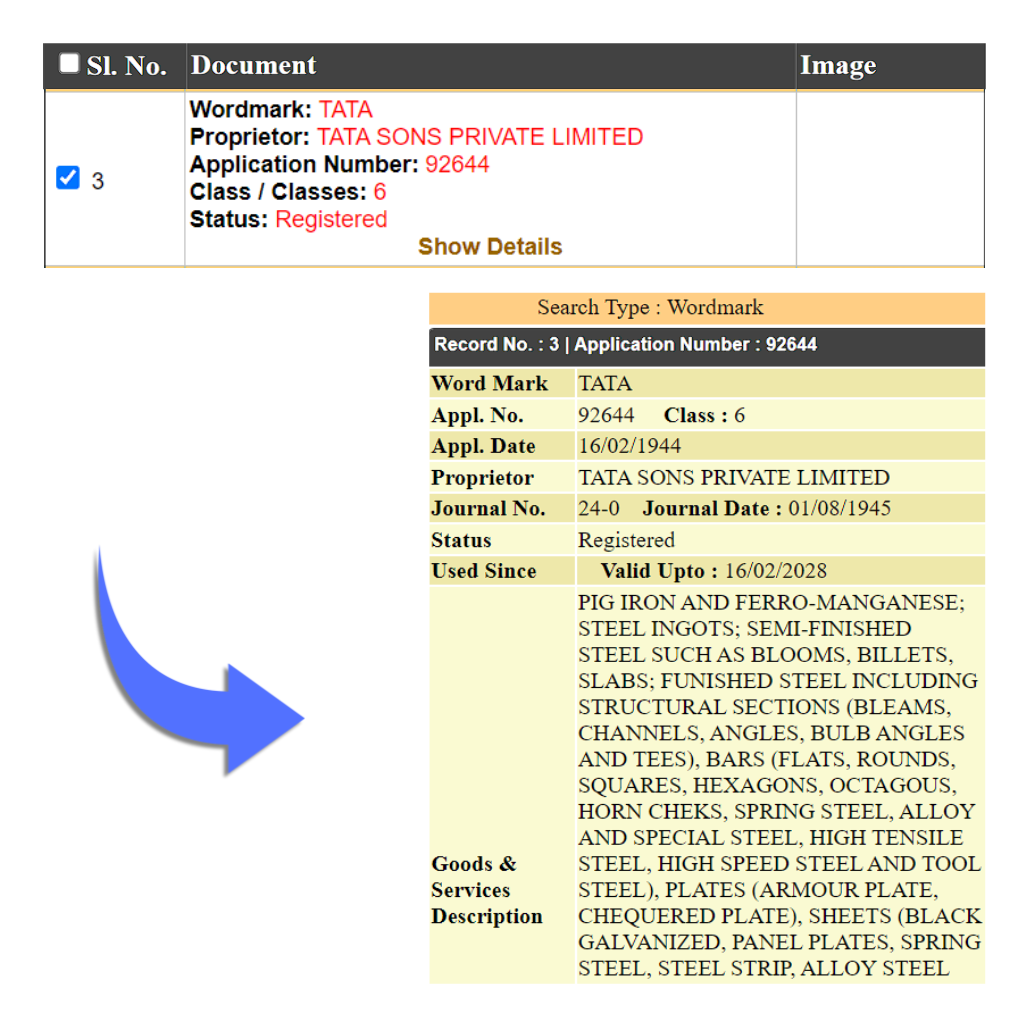
Service Mark
A service mark is the same as a trademark except that it identifies and distinguishes the source of a service rather than a product. Normally, a mark for goods appears on the product or on its packaging, while a service mark appears in advertising for the services. Service marks are often slogans. It helps differentiate services that are available in the market. E.g. LIC
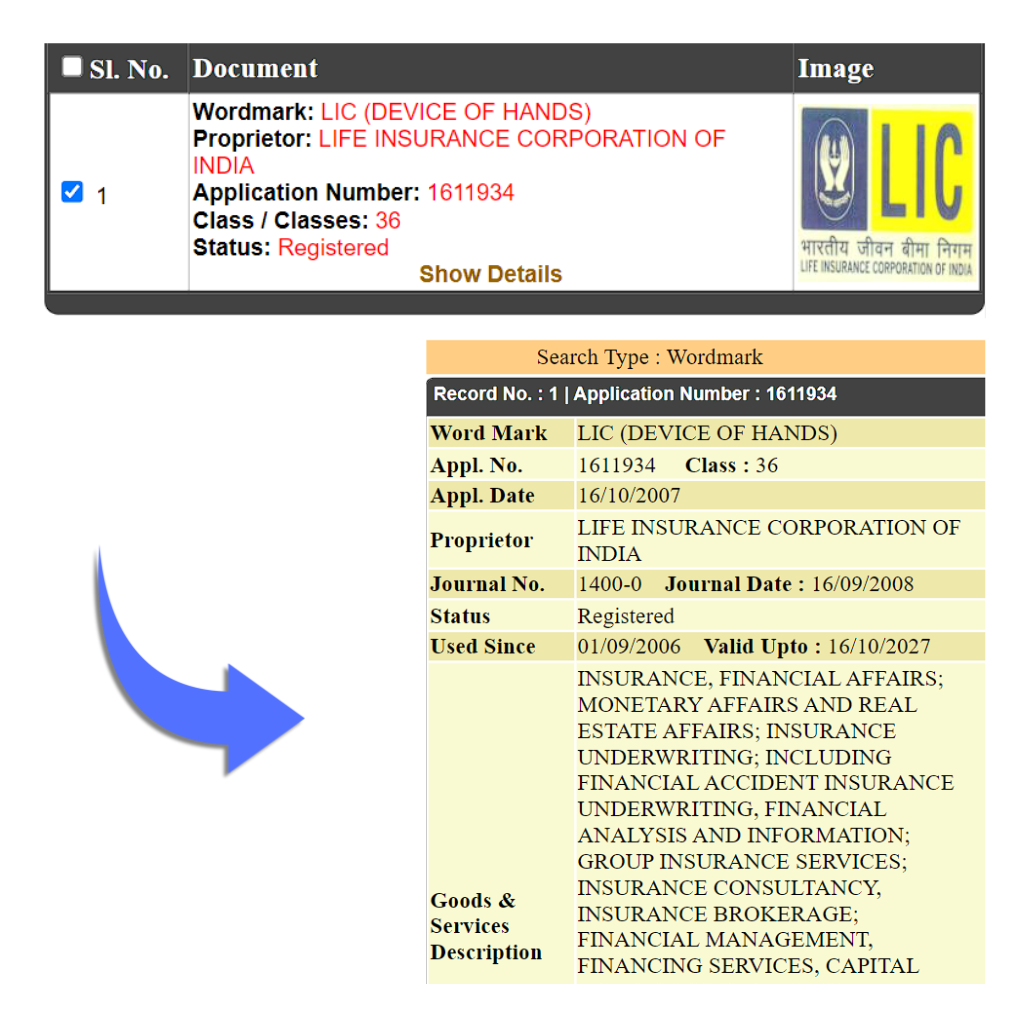
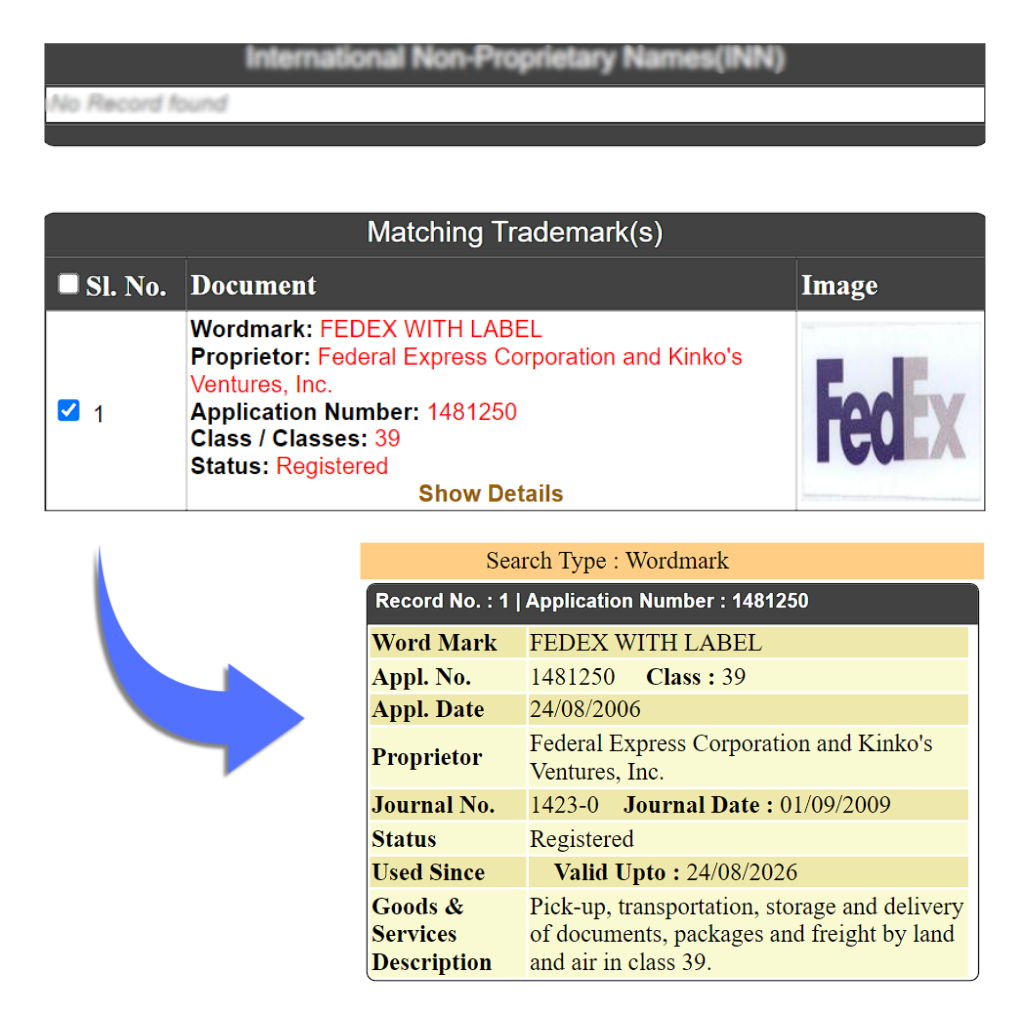
Word and Services Mark – Word and Services Mark can be together used to identify the products and services of a trading company or company proving such services. Eg: Fedex, Zomato
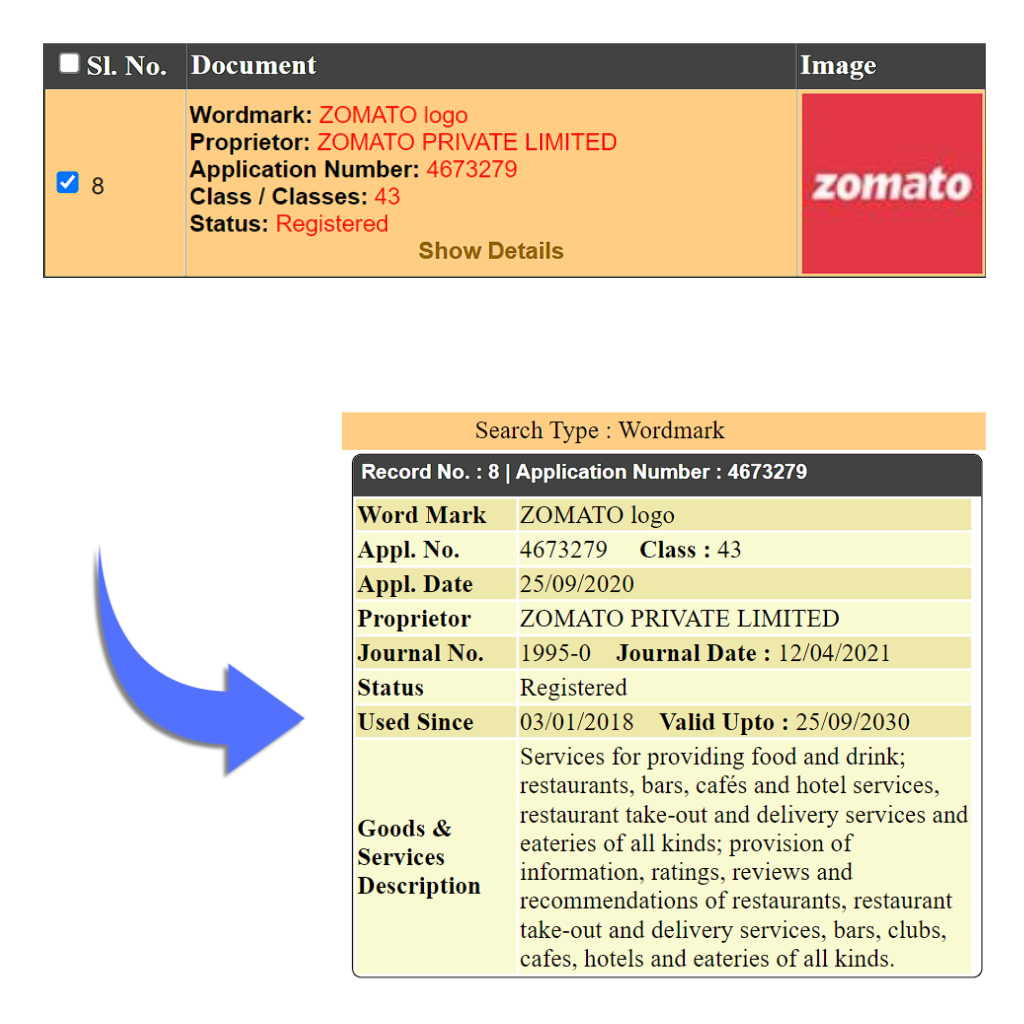
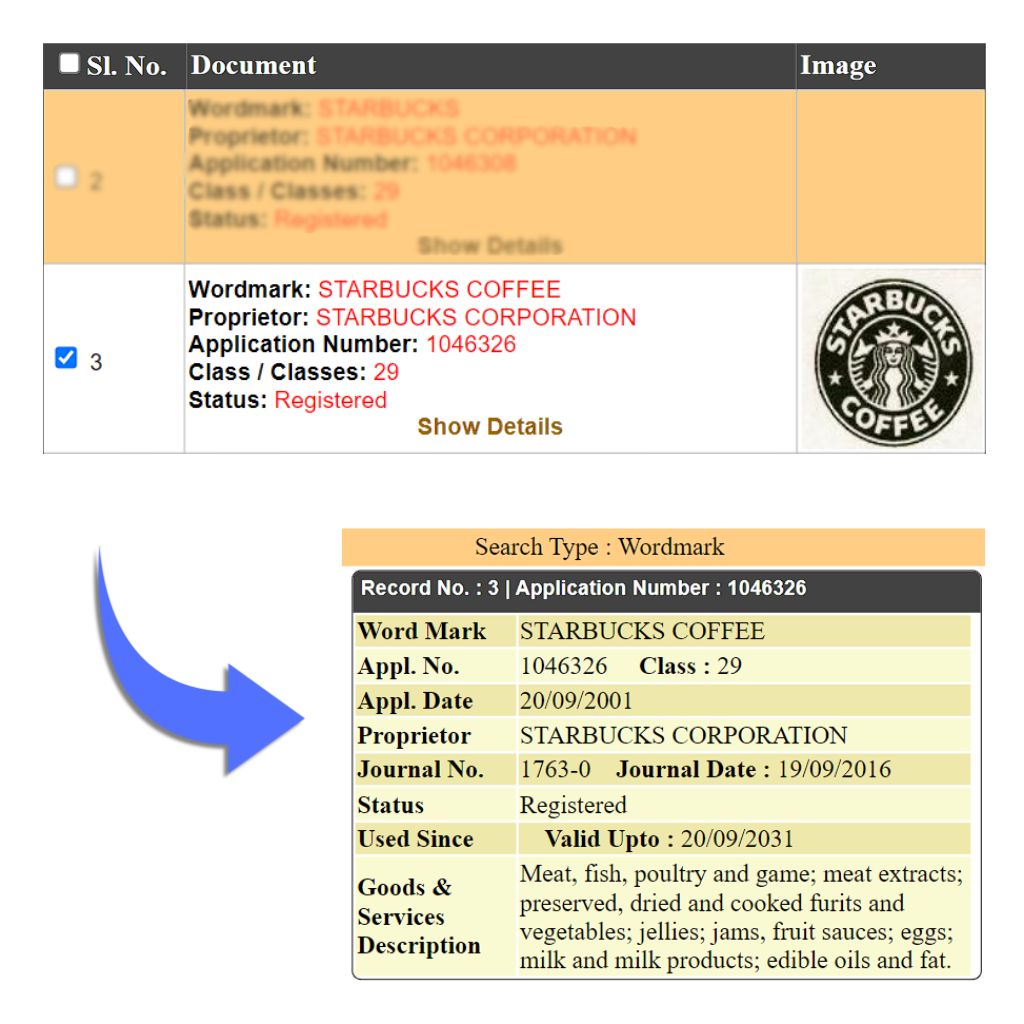
Device Mark
A device Mark is also known as a logo mark. Logo marks are those which would represent your brand or company brand in the market. These are specially used for marketing purposes. It is assumed by the people that once we have registered the logo, we need not register the word mark or vice versa. But that is not the case. A company has to register its brand name in the text form that is Word Mark and also its Logo that is Device Mark both separately.
Eg: Starbucks, Paytm
Colour Mark
A unique and distinctive Trademark with catchy colors that can be easily distinguished by consumers. However, in practice, a combination of colors stands a better chance of registration, provided that it is capable of distinguishing the goods of one trader from those of another. The company registers their colour schemes/combinations used in the brand name. Even if they upgrade or change their logo they do not change the colour scheme. Eg: Microsoft, Pepsi, Amul
Shape Mark (Trade Dress)
Shape Mark is also known as Trade Dress. It means that if a company has a product in a unique shape or patterns, then they can register that pattern or shape easily to differentiate. It is such a type of design where a customer can recognize it as to which brand it belongs. In order for protection to be approved, the shape must be significantly different from what is common in the market. For example, Coco Cola Bottle, Kitkat Chocolate
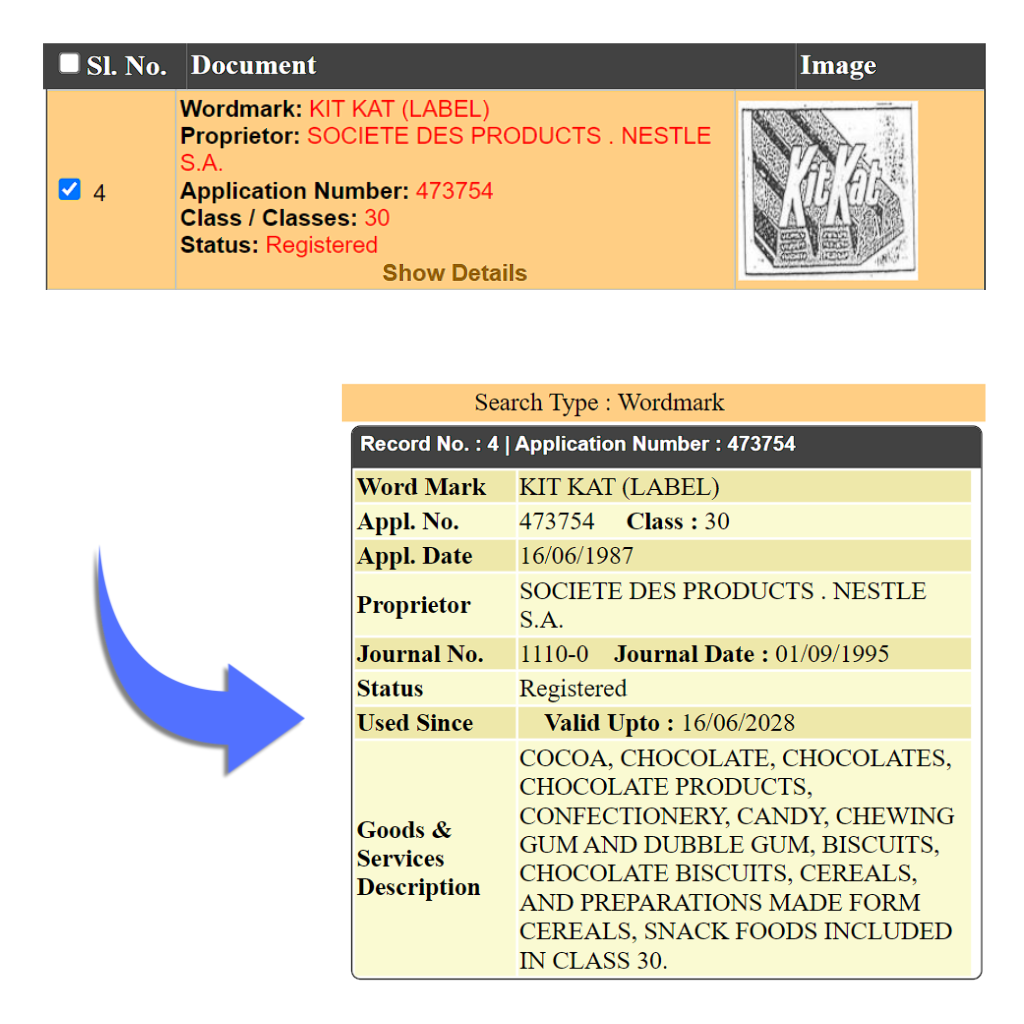
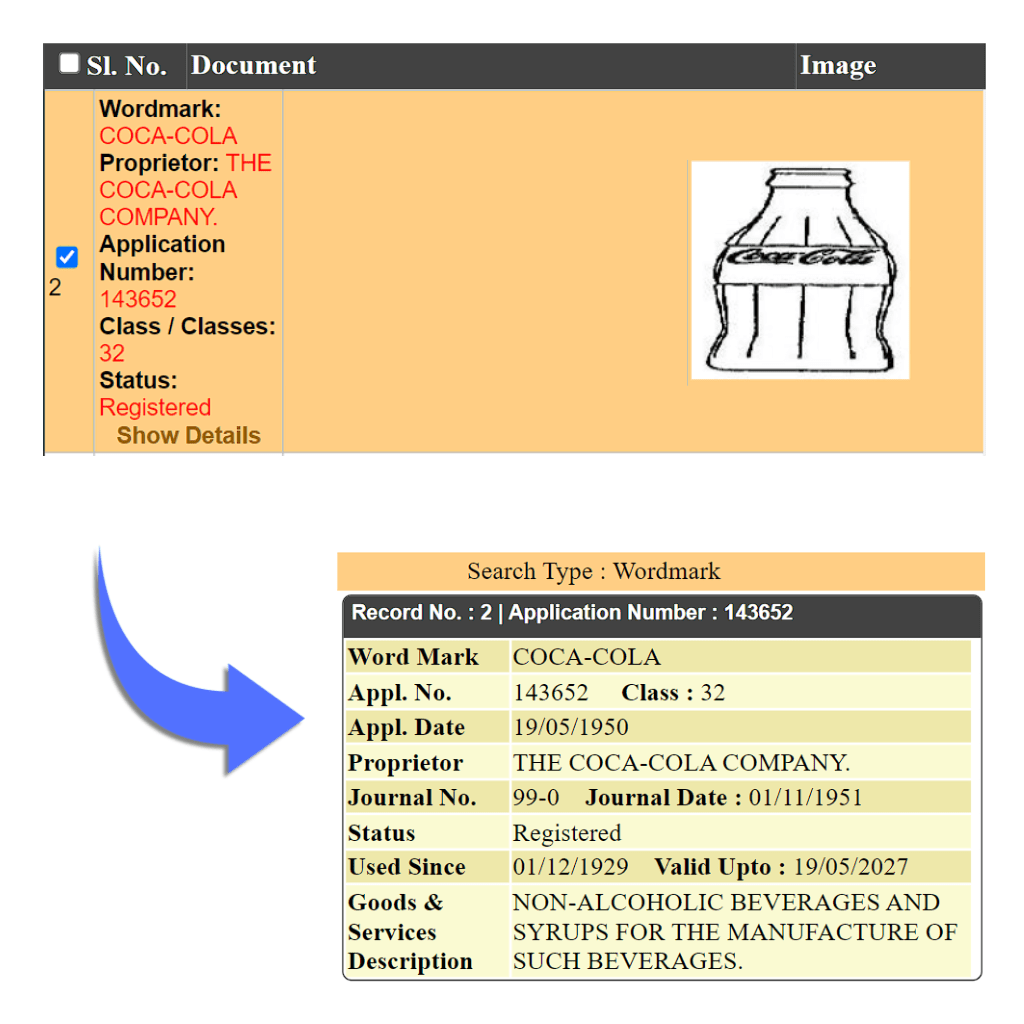
Sound Mark
These are sounds or tunes that the company has created and are registered. The function of a sound Trademark is to uniquely identify the commercial origin of products/ services by means of an audio clip. In general, applications in the form of musical notations describing the sound meet these requirements like musical notes, whereas onomatopoeic descriptions do not like the noise of a dog barking. Eg Nokia Tune, MGM Lion Roar Sound
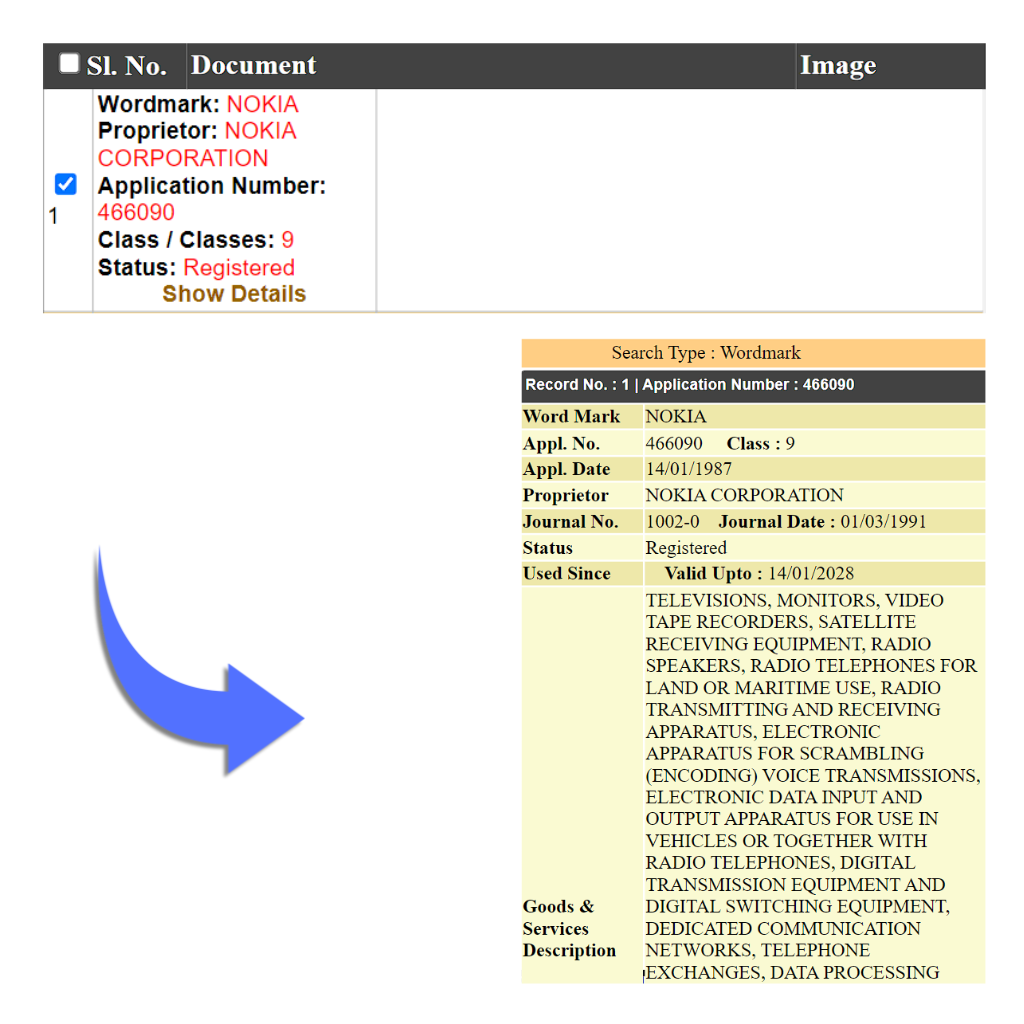
Eg: Nokia’s Sound
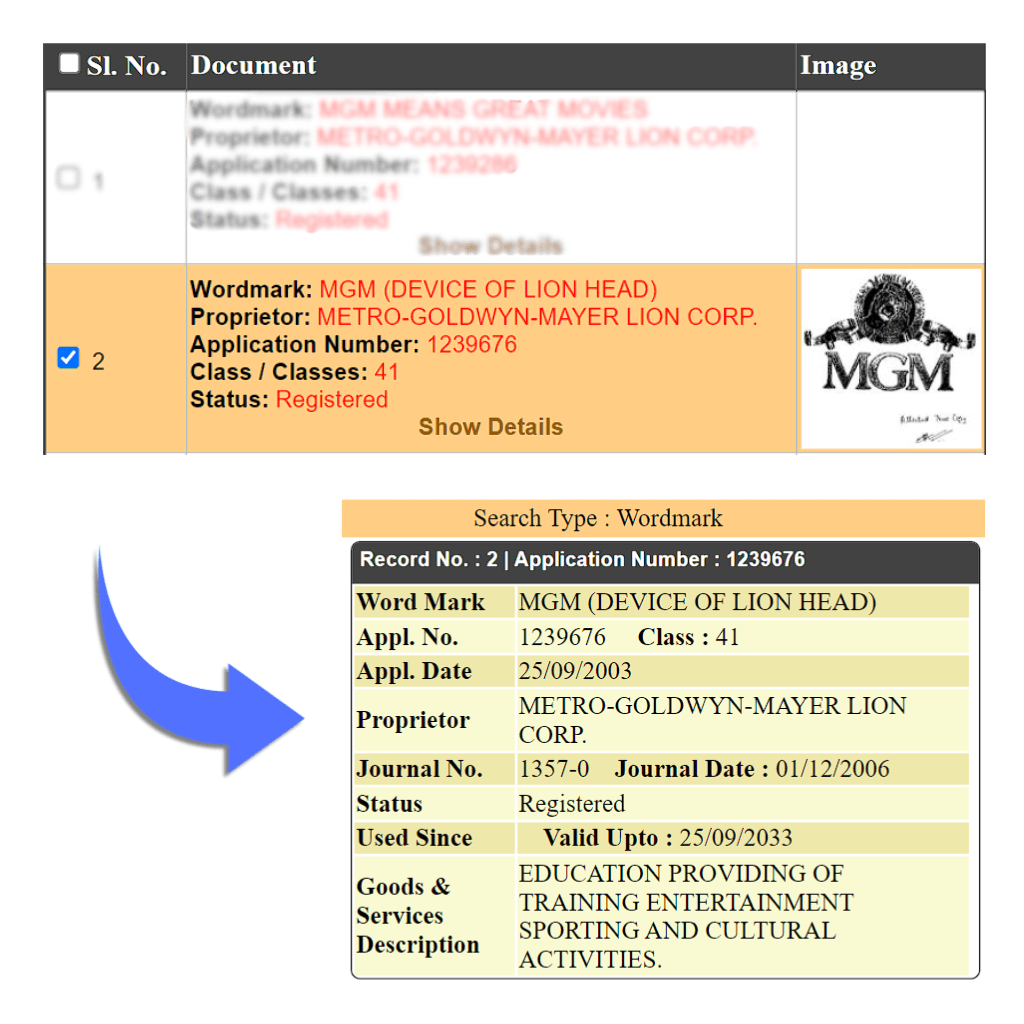
Eg: MGM’s Lion Head
Motion Mark
These are 3D or moving trademarks that consist of a combination of moving visuals with audio. The requirements of registering a motion trademark are a Textual explanation of the mark and a drawing of deception at a single point in the movement Eg: Nokia Connecting Hands.

Pattern Mark
These are the marks consisting of a pattern that is capable of identifying the goods or services of one and thus distinguishing it from those of another. Such goods/services are registrable as Pattern Marks. The pattern of such a brand is distinguishable from the products of other brands.

Certification Mark
Certification marks are essential trademarks that are used to certify that the goods or services on which they are affixed comply with certain quality, standards prescribed by a certifying entity. Such certifying entities, upon fulfillment of those quality standards, license the certification marks to be used. Basically, a certification mark on a commercial product indicates the existence of an accepted product standard or regulation and a claim that the manufacturer has verified compliance with those standards or regulations. Eg ISI, FSSAI

Collective Mark
A collective mark means a Trademark distinguishing the goods or services of the members of an association of persons not being a partnership firm, used by its members to identify themselves with a level of quality or accuracy, geographical origin, or other characteristics set by the organization.
In India, there are several organizations who have their own logo/marks. If someone is registered with that organization then they are eligible to use that mark. Since you have registered with such an organization, they provide the rights to use their mark. Whereas the trademark belongs to an individual but a collective mark belongs to an association of persons, other than a partnership firm. Eg CA, CS, Advocate.

Series Mark
When the brands are famous and popular in the market and if such brands want to open a new company under the same brand name, then instead of giving it a new name they prefer old popular brans names to the new companies to get recognition in the market without spending much on branding and marketing. Eg: McDonald has series marks incorporating the term “Mc” like Mc chicken, Mc Café, Mc Donuts etc.

Well-known Trademark
A well-known trademark refers to a mark that is recognized by the relevant public for its distinguished goods or services. It goes beyond geographical boundaries and is known across the nation or globally, even beyond the business sectors in which it operates. Recognition, reputation, and the duration of use contribute significantly to a trademark’s status as well-known.
This recognition means that the use of the mark in relation to different goods or services could lead to a perception of a connection between those goods or services and the person using the mark for the original goods or services. A mark designated as well-known enjoys enhanced protection. The Trademark Act, 1999 imposes a duty on the Registrar to safeguard well-known marks from identical or similar trademarks.
Eg: A well-known trademark is the “Nike” logo, often referred to as the “Swoosh.” This symbol is recognized globally and is synonymous with athletic footwear and apparel.

Important Points to be Noted while registering types of trademark
Non-Distinctive in nature
Marks that are devoid of any distinctive character, that is to say, not capable of distinguishing the goods or services of one person from those of another person.
Colour
Section 10 of the Act states that a trademark can be limited to a particular colour or combinations of colours. However, such limitation as to colour will only be allowed on determining the distinctive character of the mark. However, if no colour has been specifically claimed, then it shall be deemed to be registered for all colours.
Names and Surnames
Names or surnames cannot be used as a trademark in India if they do not possess a distinctive character. In the case of Prathiba M. Singh v Singh and Associates 2014. The court observed that “‘Singh’ is a very common surname, and nobody can have a monopoly over it.”
Sound
Musical notes in the form of musical notations are accepted as trademarks in India, but noises such as birds chirping cannot be trademarked. An example of a Sound trademark is the Nokia Jingle.
Smell
A Smell cannot be registered as a trademark in India. It is difficult to distinguish between different smells. However, smell marks are rare breeds. There have been very few registrations of smell trademarks all over the world which include bubble gum scent for sandals, and strawberry, cherry, and grape lubricants for combustion engines.
Shape of Goods
Section 9(3) of the Trade Marks Act, 1999 provides that, a mark shall not be registered as a trademark if it consists exclusively of—
- The shape of goods which results from the nature of the goods themselves; or
- The shape of goods which is necessary to obtain a technical result; or
- The shape which gives substantial value to the goods.
Process for registering Types of Trademark in India
Initial Trademark Search
Before starting with the registration process, a detailed Trademark Search is required to be conducted to ensure that the proposed trademark is unique and does not conflict with existing trademarks. Search can be carried out online through the official website (https://tmrsearch.ipindia.gov.in/tmrpublicsearch/) of the Trademarks Registry.
Prepare and Draft the Trademark Application
For preparing and drafting the trademark application form (TM-A), the following information and documents are required to be collated:
- A clear representation of the trademark
- Details of the applicant, including name, address, and nationality
- Description of goods or services associated with the trademark
- Date of first use (if applicable)
- Power of Attorney (if filed through an attorney)
- Digital Signature of the Applicant
The application can be filed online through the official website or a physical application can be submitted at the nearest Trademarks Registry office.
Submit the Application
The trademark application can be submitted online or offline by paying the requisite fees. The fee varies depending on whether you’re an individual, a startup, a small enterprise, or a large corporation.
Examination by the Trademarks Registry
The Trademarks Registry will review the application to ensure it complies with the relevant laws and regulations. They will assess the distinctiveness of the mark, potential conflicts, and other requirements.
Publication in the Trademarks Journal
If the Registrar finds no objections or issues with your application, your trademark will be published in the Trademarks Journal. This publication allows interested parties to oppose the registration within a specific period (usually four months).
Objection and Opposition Period
During the publication period, objections or oppositions can be filed by third parties against the proposed trademark. If an objection is filed, the opportunity to respond shall be granted.
Registration Certificate
If there are no valid objections or if you successfully resolve any objections, the Registrar will issue a Certificate of Registration for the trademark. This certificate confirms your exclusive rights to the mark.
Conclusion on Types of Trademark
Trademarks play an essential role in intellectual property rights by serving as unique identifiers for goods and services. They come in various forms, including product marks, service marks, word marks, and device marks, each with its own application and significance. For instance, product marks help differentiate commodities, service marks represent services, word marks consist of words or characters, and device marks include logos or designs.
Therefore, understanding different types of trademark is essential for protecting your brand and its unique identity. Are you looking for trademark registration & want to know more about Types of Trademark ? At Registration Arena, our expert team is here to guide you through the process. Contact us today to start the Trademark Registration process in India smoothly and efficiently.








