The second innings of Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s government presented the Union budget 2020. The Union Budget 2020 was presented by the Finance Minister Smt. Nirmala Sitharaman on 1st February. The Union Budget 2020 took a lot of audience by surprise. The lengthy presentation had few key points that were crucial in examining the upcoming financial conditions in India. The budget presented few crucial points that will determine the fate of India’s economy.
The radical Income Tax reforms presented by the ministry of finance include the key points of introducing the new and simple tax regime. Also, the changes proposed in the Union Budget 2020 are done keeping in mind the foregoing deductions and the eradication of Dividend Distribution Tax. Various changes are being done that aims to provide India, a better financial status in the world. The main aim of the Union Budget 2020 will be to add India into the $5 trillion economies of the world. The Finance Minister developed a million dollar farm, infra healthcare sectors development package that aims at growth of the country.
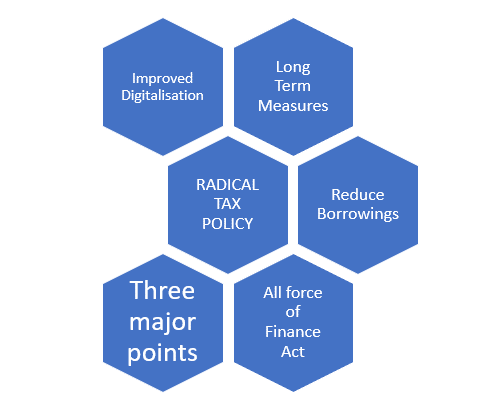
The Various Key Points of Radical Tax Policy in Union Budget 2020
- The government has focused on the improvement of the digitalized systems to levy and collect the taxes. The systems will face increase in the use of data analytics and human interface. This would help people easily understand and pay their taxes.
- The budget was focused on lifting the sagging economy and the low GDP of India. Many people were shock to see this as they were expecting short term measures to do so, but as per the budget, the ministry will focus on long term structural measures.
- The government borrowings will reduce and there are norms to reduce the fiscal deficit to 3.5%.
- The three points that were aimed by the Minister are Aspiration, Economic Growth and Caring Society.
- The proposals can be adopted by Parliament and passed under the Finance Act. The all force of these reforms will come in the Assessment Year 2021-2022 and Financial Year 2020-2021.
The Key Highlights of the Budget are discussed as follows. We have tried to incorporate the correct information from various sources.
Direct Taxation (Income Tax) in Union Budget 2020:
The various amendments and key points regarding the direct tax levy and collection policies are as follows:
- Government has introduced a major change under Section 115BAC that shows that there is an option for the taxpayers to choose from the two sets of tax slabs rates. The old one and the new one. The Taxpayers can choose from both the options. However, few of them will not be able to change it back.
- The startup owners with Employee Stock Option Plans (ESOPs) can save themselves from paying taxes for the first five years of their operation from the time they start till the time they leave the operation or sell the shares.
- Turnover threshold for audit of MSMEs increased from existing rupees one crore to five crore.
- At the same time, startup definition in terms of turnover has been increased to Rs. 100 crores from Rs. 25 crores.
- The Corporate tax for upcoming manufacturing companies brought down to 15% and for the existing companies, it is 22%.
- Individuals with income up to 5 lakhs are exempted to pay the taxes.
- All charity organisation will be issued Unique Registration Number (URN).
- It is also now necessary for Central Board of Direct Taxes (CBDT) to adopt the taxpayers’ charter, the details of which will be provided in future.
- For opening a charitable organisations, there will be provisions for providing three years of provisional registration for 3 years of operation.
- Corporative societies are now exempted to pay the Alternate Minimum Tax (AMT).
- Out of 100 deductions and exemptions, 70 are removed and the rest will come into radar in the following months.
- Interest paid withholding tax rate is reduced to 5%. This is to make available the foreign funds.
- Dividend Distribution Tax removed and classical system of dividend taxation adopted.
The Simplified Tax details for FY 2020-2021 in Union Budget 2020 are as follows:
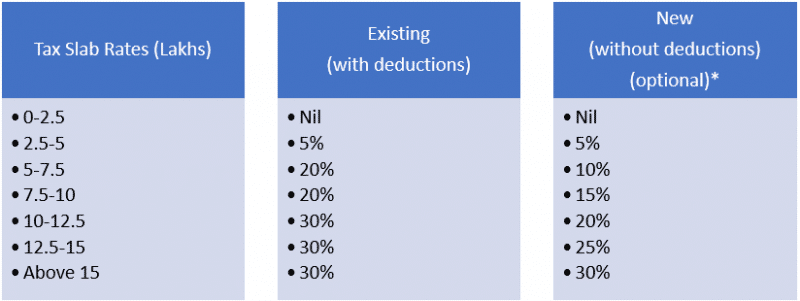
Note : If you have income up to Rs.5 Lakh only. You are eligible for rebate max of Rs. 12,500 u/s 87A thus NO TAX on income up to Rs. 5 lakh.
*The new Tax regime shall be optional for the taxpayers. An individual who is currently availing more deductions and exemption under the Income Tax Act may choose to avail them and continue to pay tax in the old regime.
Indirect Taxation (GST and Custom) in Union Budget 2020
- The new GST rate structure will now address the issue of inverted duty structure.
- The taxpayers will undergo Aadhaar verification to clear out any non-existent units.
- The custom duties on certain raw materials life chemicals have been reduced.
- Simpler ways to file GST returns like SMS feature for filing the Nil return and improvement in tax credit flow.
- The custom duties on imports of lightweight coated paper is reduced from 10% to 5%. The same is the case with news print.
- The excise duties on cigarettes and tobacco increased with no change in those of bidis.
- On the imports of medical devices (accept those exempted by BCD) will face a 5% health cess.
- Custom duty raised on furniture goods and footwear.
The budget also focussed primarily on various sectors. The prime motive of development was kept in mind and all the provisions were amended accordingly. The major focus was on three sectors : Agriculture, Infrastructure and Healthcare. However, following are some sectors which gathered attention :
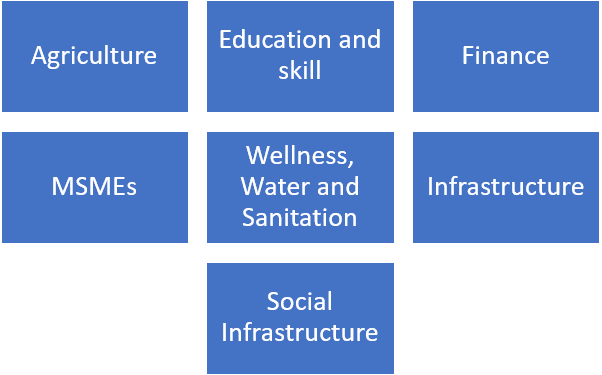
We will go through the analysis of all these sectors :
Agriculture:

- Keeping in mind the fact that 70% of India’s economy is still working on agriculture, various reforms have been made in the same sector.
- The government is aiming at doubling the farmer’s income by 2020. At the same time, it is determined at helping farmers solarise their pump sets.
- The budget also lists some programs that will help the farmers to transport the perishable farm goods from one place to another like “Kisan Rail” and “Krishi Udaan”.
- The government plans on increasing artificial insemination coverage to at least 70%. The sectors other than farming were considered. For example it is aimed to increase the exports in fishery by 2025-2025.
Education and Skill:

- The government has always been going through many projects to increase the education and school attendances of its children. However, there have been improvements, but this time, the government is aiming for even more.
- At least 150 institutes for higher education will start offering embedded courses. The students who are seeking for employment abroad will be offered special bridge courses to improve major skills.
- Under India Programme, Ind-SAT will be conducted in Africa and Asia. The government is planning to allocate 99,300 crores rupees for educational sector for the FY 2020-2021. Around 3,000 crore rupees will be devoted for skill development.
- National Mission on Quantum Technologies and applications with an outlay of Rs.8000 crore proposed.
Finance:

- Finance sector also faces a lot of reforms. The Deposit Insurance Coverage will be increased from 1 lakh rupees to 5 lakh rupees per depositors. The NPS Trust will be now separate for all government employees from PFRDAI.
- There is also a proposal to sell the government’s balance holding in IDBI Bank. A major point to note is that there have not been much reforms in the financial sector.
- Specified categories of government securities would be opened Specified categories of government securities would be opened for non-resident investors.
- FPI Limit for corporate bonds to be increased to 15 per cent.
- New debt ETF proposed mainly for government securities.
- Eligibility limit for NBFCs for debt recovery under SARFAESI Act proposed to be reduced to asset size of `100 crore or loan size of 50 Lakh.
MSMEs:

- The new amendments are planned for the Factor Regulation Act, 2011. The new amendments made will allow NBFCs to increase invoice financing to MSMEs. For the same, there has been a provision of offering a subordinate debt for MSMEs by banks which is shown under Guarantee Trust.
- The debt will be counted as quasi-equity. The application based invoice generation for MSME has been introduced that will help them financing the new products easily.
- This will further decrease the problems of delayed payments and cash flow mismatches.
- Scheme to encourage manufacturing of mobile phones, electronic equipment and semiconductor packaging.
- National Technical Textiles Mission for a period of 4 years.
- NIRVIK Scheme for higher export credit disbursement launched.
- Setting up of an Investment Clearance Cell to provide end to end facilitation.
- Extension of invoice financing to MSMEs through TReDs.
- Scheme anchored by EXIM Bank and SIDBI to handhold MSME in exports markets.
Wellness, Water and Sanitation:

- Under the PM Jan Arogya Yojana, more than 20,00 empanelled hospitals have been constructed. The “TB Harega Desh Jeetega” campaign will be launched by 2025 to end TB in various parts of country.
- The government will focus on increasing the numbers of Jan Aushadhi Kendra Scheme at all districts by 2024. The focus will drive the liquid and greywater management initiatives along with the practices of waste management.
- Viability gap funding proposed for setting up hospitals in the PPP mode.
- Focus on liquid and grey water management along with waste management.
- More than 20 000 empanelled hospitals under More than 20,000 empanelled hospitals under PM Jan Arogya Yojana.
Infrastructure:

- To launch National Logistics Policy.
- Roads : Accelerate the development of the Highways.
- Railways : The reforms in Railways include that the 150 passenger trains will go in PPP Model. More “Tejas” type trains will get developed.
- Port : Planning to commercialize at least one port.
- Air: 100 more airports to be developed under UDAAN.
- Power: Efforts to replace conventional energy meters by prepaid smart meters.
- Gas Grid: Expand National Gas Grid to 27,000 km
- Infrastructure Financing: 103 lakh crore National infrastructure Pipeline projects announced.
- An international bullion exchange to be set up at GIFT City.
Social Infrastructure:

- Women and child social welfare :
-More than 6 lakhs of anganwadi workers were provided with the cell phones.
-A team will be appointed to lower the MMR and improving the nutrition levels.
- Culture and Tourism :
-Establishing the Indian Institute of Heritage and Conversation.
-Establishing a museum for the Numismatics.
-To set up Tribal Museum in Ranchi.
-To set up Maritime museum in Lothal
- Environment Caring Society child, social Welfare
-Coalition for Disaster Resilient Infrastructure equipped with smart phones. Encouragement to states implementing plans for cleaner air in cities above 1 million.
Conclusion
This year’s budget speech had been the longest in the history. It ran for 2 hours 42 minutes which was a lot to handle for our ministers. But the speech and presentation was informative and it focussed on key areas like education and infrastructure that need to be taken care of. A lot of amendments were discussed which are aimed at making our country to catch up with the economic paces of the rest of the countries in the world. India has been facing a sagging economy but the government, through its budget has promised to try its best to pace up as far as the economic development is concerned.
For more information, visit : https://www.indiabudget.gov.in/.







