We all know that farmers play an important role in our life. In fact, not only in our lives, their role is significant in the agriculture-dominated economy of India. Farmers can organize their business structure typically in two different forms of entities. First is FPO i.e., Farmer Producer Organization, and Second is FPC i.e., Farmer Producer Company. In this blog, we will discuss the meaning of and the difference between FPO and FPC.
Farmer Producer Organization (FPO)
Producer Organizations are legal entities that can be formed by primary producers such as farmers, fishermen, milk producers, artisans, etc. The producer organization in which all the members are farmers is known as Farmer Producer Organization or FPO.
In simple words, FPO is formed when farmers come together by pooling their resources to jointly tackle various issues related to farming such as sourcing of input, availing credit facilities, deployment of technology, etc. In India, two forms of FPO are popular viz. Cooperative Society and Producer Company.
Features of Farmer Producer Organization
The following are the features of Farmer Producer Organization –
- It is formed by a group of farmers.
- FPO deals with activities related to farming such as supply of farm inputs, dissemination of market information, etc.
- It operates for the benefit of its members i.e., farmers.
- Profits of FPO are shared amongst farmers.
Advantages of Farmer Producer Organizations
The following are the advantages of a Farmer Producer Organization –
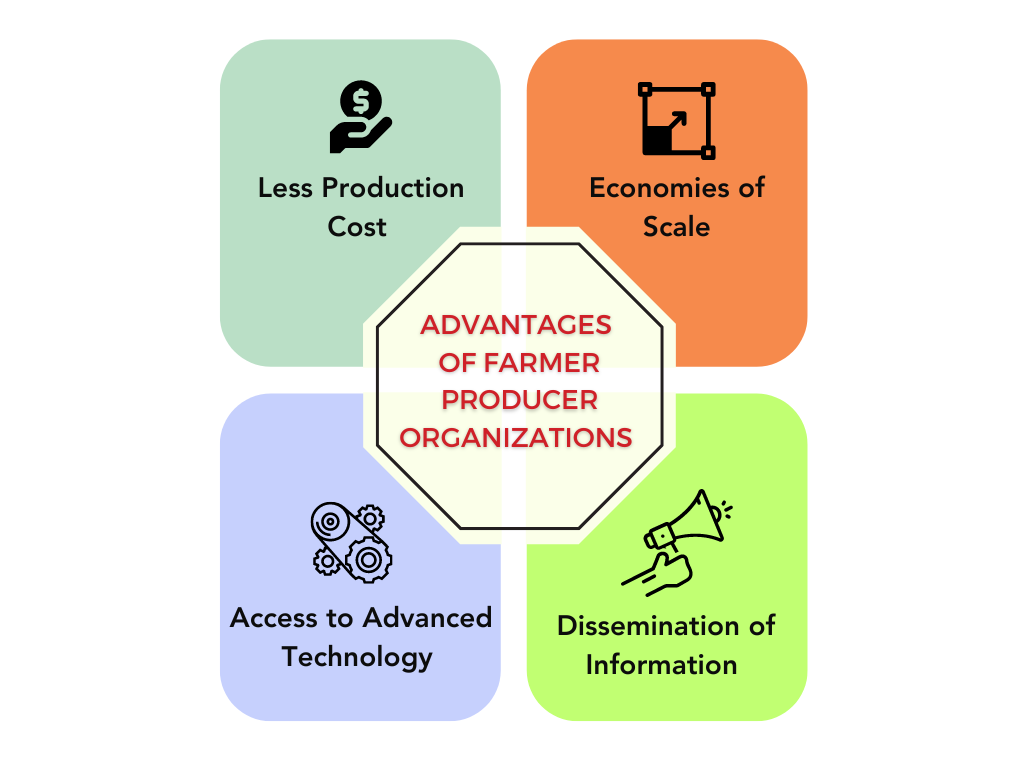
Less Production Cost
An FPO can procure all the farm inputs in large quantities at wholesale rates for farmers. Therefore, the cost of raw materials reduces which in turn leads to lower cost of production for farmers.
In addition, members of FPO can use custom hiring services for farm equipment.
Economies of Scale
FPO brings along the benefit of economies of scale as production takes place at a large scale. Due to this benefit, the sales price of finished products is less and traders and retailers are likely to get attracted to an FPO.
Access to Advanced Technology
Through FPO, farmers can get access to modern and advanced technology. The adoption of technology helps them in carrying out different processes like pest resistance, irrigation, etc in an efficient manner.
Moreover, FPO also fulfills the infrastructure and marketing needs of farmers.
Dissemination of Information
FPO educates farmers and provides them with information regarding the prices of crops and the volume required in different locations. Therefore, farmers can develop a market understanding with the help of FPO.
Farmer Producer Company (FPC)
When a Farmer Producer Organization is formed and registered as a company, it is known as Farmer Producer Company or FPC.
Definition as per Companies Act, 2013
As per Section 378A(l) of the Companies Act, 2013, a Producer Company means a body corporate that has its objects or carries out activities as given in Section 378B and which is registered as a Producer Company under the Companies Act, 2013 or Companies Act, 1956.
Objects of a Farmer Producer Company
Section 378B of the Companies Act, 2013 contains the objects of a Farmer Producer Company. To be classified as a Farmer Producer Company, a company must carry out any one or all of the objects such as –
- Production, procurement, harvesting, pooling, grading, marketing, handling, selling, or export of primary produce of its members; or
- Import of products or services for members’ benefit; or
- Processing such as drying, brewing, preserving, distilling, vinting, canning, and packaging of the produce of members of the company; or
- Manufacturing or supply of machinery, consumables, or equipment to the members; or
- Imparting education regarding principles of mutual assistance to members and others, etc.
Requirements for Formation of FPC
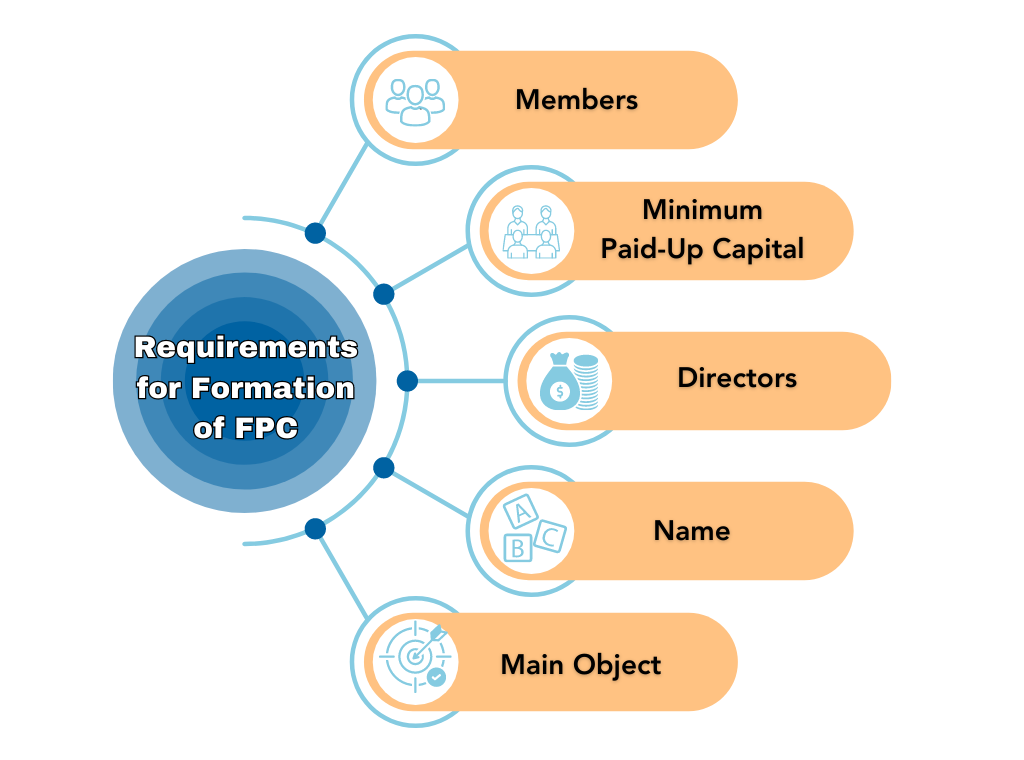
The following are the requirements for the formation of a Farmer Producer Company –
Members
A minimum of 10 individuals, who are producers or two or more producer institutions or a combination of ten or more individuals and producer institutions are required to form a Producer Company.
Directors
A Producer Company shall have a minimum of 5 directors on its board.
Minimum Paid-Up Capital
There is no limit specified in law as to the minimum paid-up capital of a Producer Company. However, the share capital of such a company shall consist of equity shares only.
Name
The name of a Producer Company shall end with the words “Producer Company Limited”.
Main Object
The main object of a company intending to be classified as a Producer Company shall be any one or more of the objects mentioned above.
Advantages of Farmer Producer Company
The following are the advantages of a Farmer Producer Company –
Limited Liability
The Memorandum of Association (MOA) of a Farmer Producer Company shall state that the liability of its members is limited. Therefore, in case the company incurs losses, the members of an FPC are liable only up to the unpaid amount on shares held by them. The creditors cannot recover their debt by selling the personal assets of members.
No Limit on Maximum Number of Members
Although a Farmer Producer Company functions like a Private Company, there is no limit on the maximum number of members. Therefore, there are more chances of expansion as the number of members can be increased anytime and additional capital can be raised.
Support from Government and Other Organizations
Farmer Producer Companies receive support from the government in the form of different schemes and tax deductions, for example, PM Kisan FPO Scheme 2023, deduction under Section 80 PA of Income Tax Act, 1961 on profits and gains of producer companies, etc. In addition, organizations like NABARD, SFAC, NAFPO, etc. also work for the benefit and welfare of FPOs.
Financial Assistance to Members
Farmer Producer Company can provide financial assistance to its members in the form of credit facilities, loans, advances, etc. However, it shall be subject to the Articles of Association (AOA) of the company.
Read more: Annual Compliances of Farmer Producer Company
Difference between FPO and FPC
Now that we have understood what are FPO and FPC, let us discuss the difference between the two.
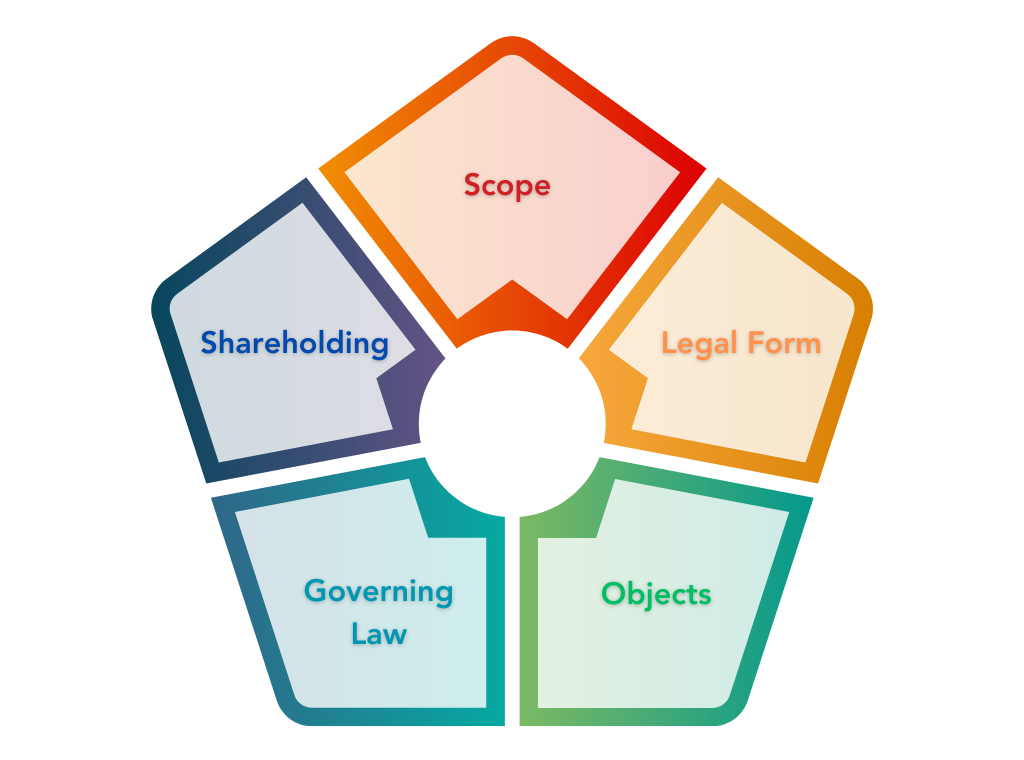
Scope
The scope of FPO is wide while the scope of FPC is narrow.
Legal Form
FPO can take any one of the several legal forms such as Cooperative Society, Company, etc.
FPC shall be in the form of a company only.
Objects
Farmer Producer Organizations can have different objectives such as extending support to members, procurement of input for members, marketing of produce, etc.
While a Farmer Producer Company shall carry out only those objects as specified under the Companies Act, 2013.
Governing Law
In the case of FPO, the governing law or statute depends on the legal form that the FPO takes.
On the other hand, the Companies Act, 2013 governs farmer-producer companies.
Shareholding
Members contribute capital in an FPO, but shares are not allotted to them except in the case of a company.
While shares are allotted to the members of a Farmer Producer Company.
Conclusion
Forming a Farmer Producer Organization or Farmer Producer Company is beneficial for farmers. It helps them to organize themselves legally and access the funds, inputs, and technology that they require. However, it is necessary to be aware of the difference between FPO and FPC so that you can take the right decision for your business.
At Registration Arena, we are having a team of experts like CA, CS, and other professionals who can help you in the FPC Registration as well as in compliance with regulatory requirements. Our team can also assist you in obtaining different registrations like GST, Trademark, etc.
Call us now at +918600544411/22 or drop an email at sales@registrationarena.com for more information.








