Fund management in a company is one of the most crucial decisions that the management has to make. To manage the funds, it is important that the management knows where they can raise money and how to utilize the funds so as to generate passive income for the company.
Companies may adopt various methods to utilize excess funds; one such method is giving loans to other companies for their business. It will not only improve the business relations but the company will also be entitled to interest income out of the loans provided.
In this article, we will talk about the restrictions which are imposed by the statute on the loans provided by a private limited company to other persons and body corporates.
Legal Provisions
Section 186 of the Companies Act 2013 deals with inter-corporate loans and investments by companies.
Section 185 of the Companies Act 2013 deals with Loans to directors and other related parties to directors
The term ‘loan’ is not defined in the statute but in a literal sense, it means the advancement of money with a promise to pay back.
A company may provide loans in three ways-
- Direct Loan- Giving loan to any Body Corporate or to any Person
- Indirect Loan- giving a guarantee or providing any security in connection with a loan to any person or body corporate.
- Investment- acquire by way of subscription, purchase, or otherwise securities of any Body corporate.
Providing loans in any of the aforesaid means would attract Section 186 of the Companies Act 2013. It means that the restrictions mentioned in this section are applicable if a company carries out these transactions.
Note-
- The word ‘body corporate’ shall be construed as per section 2(11) of the said Act.
- Since the term ‘person’ is not defined in the Companies Act 2013, it shall be construed as per section 2(42) of the General Clauses Act; Any company, body corporate, association, or body of individuals, whether incorporated or not.
- ‘Person’ does not include an employee who is in the employment of the company.
It means there is no restriction if a company gives a loan, and provides a guarantee and security to its employees.
Restrictions
Unanimous Board Resolution-
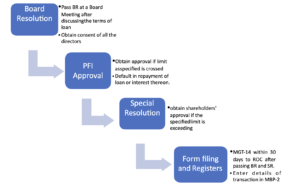
Subsection 5 of section 186 requires that the company shall call a board meeting, discuss the terms of providing the loan, investment, guarantee, or security, as the case may be, and pass a unanimous board resolution i.e., the consent of all the directors present in the meeting.
The compliance officer/directors shall ensure that the resolution shall be passed at a board meeting only and it should not be a resolution by circulation.
Special Resolution-
Section 186(2) requires the company to pass a special resolution, i.e., the consent of 75% of members present in the general meeting if the amount of loan, investment, guarantee, or security, exceeds the higher of below-mentioned limits-
- 60% of Paid-up share capital, free reserves, and security premium balance or,
- 100% of free reserves and security premium account balance
Pursuant to section 102 of the Act, the explanatory statement to the notice of the general meeting shall contain the extent of the shareholding interest of every promotor, director, manager, or other KMP in the company to whom such loan, investment, guarantee, or security is being provided if it is more than 2% of the paid-up share capital of the company.
MGT-14 shall be filed to ROC within 30 days of passing a special resolution, pursuant to section 117.
Note- Shareholders shall specify the exact amount up to which the board of directors of the company is authorized to undertake these transactions.
Special resolution not required– If a company is giving a loan, guarantee, providing security, or making an investment in its wholly owned subsidiary or a joint venture company, then a special resolution is not required to be passed.
Approval from Public Financial Institution (PFI)-
If loans are given, guarantees are given, securities are provided, and investment is made, as the case may be, up to the above-mentioned limits, then PFI approval is not required unless a company has committed a default in the repayment of a loan or interest thereon.
It means PFI approval is necessary in 2 cases-
- Company has committed default in repayment of loan or interest thereon due to PFI
- The company is undertaking the transaction in excess of the aforesaid limits.
Note- It may be noted that the company is not required to obtain approval from any other creditor except public financial institutions.
Disclosures in Financial Statements-
All the details of loans, investments, guarantees, and security, made by the company so far and the intended use of such loan, guarantee, or security by the receiver of the loan, guarantee, or security shall be adequately disclosed in the financial statements and shall be presented before the shareholders in the general meeting before passing the special resolution.
Rate of interest-
A company cannot give loans, guarantee, provide security, or make investments at a rate of interest that is lower than the yield on government securities of one year, three years, 5 years, or 10 years, closest to the tenure of the loan being provided by the company. An interest-free loan is not allowed.
No default in repayment of deposits-
Section 186(8) restricts the company from providing loans, investments, guarantees, or security if there is a subsisting default in the repayment of deposits or interest thereon. The company shall be allowed to undertake these transactions only after rectifying the default.
Maintenance of registers as prescribed-
Section 186(9), 186(10), read with Rule 12 states that, every company shall, from the date of its incorporation maintain a register in form MBP-2. It shall contain the details of loans, investments, guarantees, and securities. It has to be maintained by the company secretary. He is required to enter the details of such transactions within 7 days. It must be kept at the registered office of the company under the safe custody of the company secretary.
Members are allowed to inspect this register and collect extracts free of cost. A certified copy can be obtained by them on payment of prescribed fees.
Restriction on making investments-
As per section 186(1), a company is not allowed to make investments through not more than 2 layers of investing companies. This provision was inserted to prevent increasing money laundering cases.
However, if the company aims to acquire a company incorporated outside India that has investment subsidiaries beyond two layers, this provision will not restrict such a company from doing so.
It shall also not hinder a subsidiary company that aims to set up an investment subsidiary from complying with any other law for the time being in force.
Since investment is the ordinary course of business for investing companies and NBFCs, any investment made by them would not attract the provisions of section 186. It implies that giving loans, guarantees, and providing security are covered under the ambit of this section.
Moreover, Banking companies, Insurance companies, housing finance companies, and infrastructure companies are not governed by the provisions of this section as per section 186(11).
An investment in ‘rights share’ is also permitted.
186(6) also require that no company shall give loans to the SEBI registered companies in excess of the limits as may be prescribed.
Process of Providing Loan
Apart from these restrictions, Private Companies which do not fulfil the below-mentioned conditions are subject to some other restrictions as specified by section 185 of the companies act 2013.
- That private company in whose share capital no other body corporate has invested any money, and
- whose total Borrowing is less than twice its paid-up share capital or fifty crore rupees, whichever is lower, and
- such a company has no default in repayment of such borrowings subsisting at the time of making transactions under this section.
It implies that if a private company is not fulfilling these conditions, additional restrictions are imposed on them for providing loans, guarantees, and security, as the case may be.
These restrictions are imposed by section 185 of the Act.
1.Prohibition to give loans to directors-
The company is not allowed to give a loan, directly or indirectly to the following-
- Director of the company
- Director of holding company. Holding company shall be construed as per section 2(46).
- Relative to the director of the company. Relative shall be construed as per section 2(77).
- Relative of director of holding company
- A Firm in which the aforesaid persons are partners
- Partner of director of a company
- Partner of director of holding company.
It is to be noted that the statute has not put any kind of restrictions with respect to advancing loans, guarantees, and securities to the director or his relative of a subsidiary company or an associate company.
2. Restriction to giving loans to persons in whom director is interested-
The company may advance loan, provide a guarantee, and security to any person in whom the director may be interested subject to two conditions-
- Special Resolution at the general meeting of the company.
- The borrowing company shall utilize the loan amount for its principal business activities.
Directors may be interested in the following-
- Any private company of which any director of the lending company is a director or a member
- Anybody corporate in which twenty-five per cent or more of the total voting power is controlled by the director or directors of the lending company.
- Anybody corporate whose Managing director or board of directors or manager are accustomed to acting in accordance with the instructions provided by the directors of the lending company.
3. Loan to Managing Director (MD) or Whole Time Director (WTD) –
A loan to MD or WTD is allowed if the scheme is approved by a special resolution or if it is a part of the conditions of service extended by the company to its employees.
4. Loan to Subsidiary Company-
- Wholly owned subsidiary- Any loan advanced, guarantee given or security provided by a holding company to its wholly owned subsidiary is allowed by this section if the borrower company for its principal business activities.
- Subsidiary company- Holding company is allowed to give a guarantee or provide security in respect of a loan advanced by any bank or public financial institution to its subsidiary company only if it uses the amount for its principal business activities.
No restriction is imposed by Section 185 on companies whose principal business is providing loans, giving guarantee or security if the same is being provided at the rate of interest as specified above in Section 186.
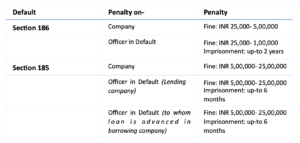
Penal Provisions (Penalty for Non-Compliance)
Registration Arena is the expert hub that can assist you with your business requirements. For more details Contact us at 8600544411 / 8600544422.








