Introduction
Agriculture in India is the most important sector of the Indian economy. This is due to its vast contribution to the nation’s GDP and employment. Around 85% of the land in India is owned by small and medium farmers producing different varieties of food and grains. For most of history, Indian farmers have been in dark regarding Farmer Producer Companies. Owing to the lack of education, all they spent their time on was sowing the seeds and waiting for the harvest to grow so that they could sell it in the market. They were unaware of the existence of such a corporate structure let alone its benefits. Through this article, we aim to tell readers All About Producer Company.
The Government introduced SFAC (Small Farmers Agribusiness Consortium) and NABARD (National Bank for Agricultural and Rural Development) to solve the problems of the farmers by organizing them into Producer Organisations (POs). The producer companies themselves can also be a part of a Producer Organisation. The producer here refers to farmers and all those agriculturalists producing food products. Forming an organisation acknowledged by the market and the government helps the member-farmers to access credit and market linkages. Collective decision making further improves the plight of the farmers.
What is a Producer Organisation? (PO)
A producer organisation is an organisation formed by the primary producers which include farmers, fishermen, weavers, milk producers, craftsmen etc. A PO can also be a cooperative society which makes available the shared profits and benefits to all the member-farmers.
Producer Company is a company registered under the Companies Act, 2013, which has the objective of production, harvesting, procurement, grading, pooling, handling, marketing, selling, export of primary produce of the Members or import of goods or services for their benefit. Produce are things that have been produced or grown, especially by farming.
The motive of a Producer Company is to ensure that the problems of the primary member-farmers are reduced by providing them adequate help and better income. Since, an individual farmer does not have enough volume of the produce to get the necessary benefits of the economy, the organisations tend to ensure a healthy division of revenue and benefits within the organisational members. By combining the profits and the surplus, the primary producers can enjoy the benefits of the economy. The unity of all the producers serves as a strong voice in the market and lets them command a better bargaining power.
Activities Carried by Producer Company
The formation and the regulation of a Producer Company follows the guidelines mentioned in the provisions of Sections 581A to 581ZL of Companies Act, 1956, read with Companies Act, 2013, and the rules made thereunder. The concept of Producer Company was first introduced in 2002 based on the recommendations of a leading economist, MR. Y.K. Alagh.
A producer company must follow the following activities according to the Companies Act 2013 (formerly the Companies Act 1956):

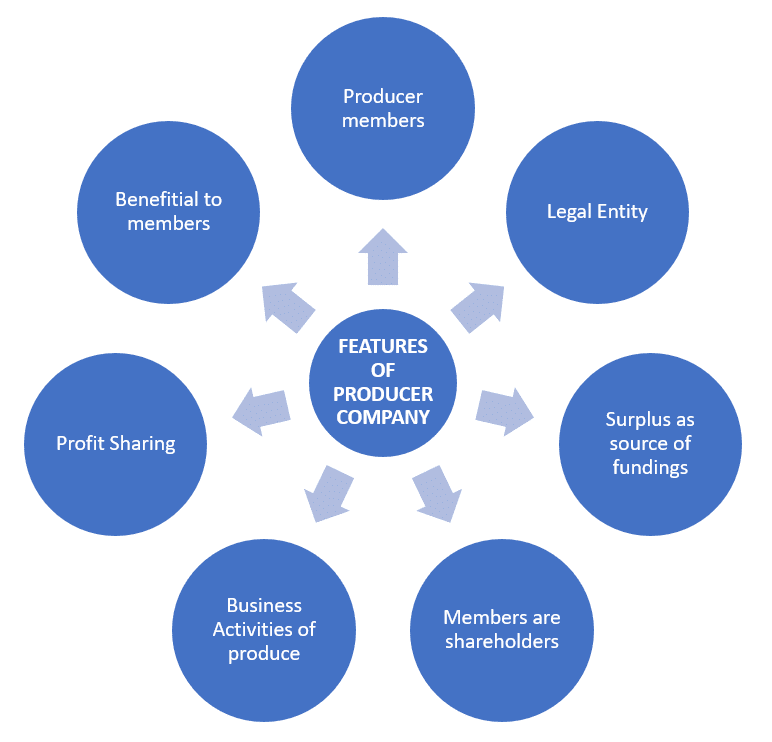
Features of Producer Company
The following are the features of the Producer Company:
- Producer members: The Producer Company is a group formed by the primary producers engaged in farm or non-farm activities.
- Legal: It is a legal entity and registered body.
- Shareholders: The producer members are the shareholders in the organisation.
- Activities: The Company deals with the business activities related to the primary product.
- Aim: The main motive of Producer Company is to benefit the member producers.
- Profit Sharing: The profit is shared among all the member-farmers.
- Funding: A part of the surplus is added to the funds of the company for business expansion.
Benefits of Producer Company
The NABARD, SFAC and other government departments aimed at producer sector benefits, support the promotion of POs. The Corporate and Domestic & International Aid Agencies have also joined hands in improving the conditions of the producers. These provide the financial and/or technical support to the Producer Organisation Promoting Institution (POPI) for promotion and hand-holding of the PO.
A PO supports the members by providing them a huge portion of the income as many middlemen in the market get removed. By aggregating the demand for inputs, the PO can buy in bulk, thus procuring raw material at cheaper price compared to individual purchase. The services provided to the members also reduce the transportation cost to the market. Thus, reducing the added cost to the produce. All the aggregate produce offers a better price per unit produce to the member-producers. The PO aims at making the members aware about the market forces and techniques for better produce. The main motive remains to provide more income to the primary producers.
The following are the benefits of the Producer company:
- Allotment of equity shares: The members can be allotted shares basis the value of produce as determined by the Board of Producer Company.
- Distributed in Proportion to produce: The withheld price may be disbursed later in cash or in kind or by allotment of equity shares, in proportion to the produce supplied to the Producer Company.

- Limited Return: Every Member shall, on the share capital contributed, receive only a limited return.
- Bonus Shares: Every such Member may be allotted bonus shares in accordance with the provisions contained in section 581ZJ.
- Reserve funding: A portion of the surplus is saved in the fund owned by the board of producer company.
- Patronage Bonus: The surplus if any, remaining after making provision for payment of limited return and reserves referred to in section 581ZI, may be disbursed as patronage bonus, amongst the Members, in proportion to their participation in the business of the Producer Company, either in cash or by way of allotment of equity shares, or both, as may be decided by the Members at the general meeting.
Difference between Producer Company, Public Limited Company and Private Limited Company
As the name suggests, the Producer Company seems to be a Public Company but as per the Companies Act, 1961, once registered, the same shall become a body corporate as if it is a Private Company and shall not under any circumstances deemed to be a Public Company. The following are the basic differences between the three forms of Companies:

Structure of Producer Company
To understand the governance of the company, it can be segregated in three major divisions as defined by the law (a detailed description follows):

- Members/shareholders: In a Producer Company, only a producer or producer institutions can acquire membership. Producer Company is a membership-based body and it can act only through its members. Thus, a company is created by the members, and can also be wound-up by them. Members acts through heir General Body.
- Board of Directors: Elected by members and may act collectively only in meetings
- Office bearers: Individual selected to look after the day-to-day affairs of the company, like CEO, accountant, go down keeper etc. They are salaried people of the company.
Management of the Producer Company
The Producer Company is managed by the Board of Directors and the Company is owned by the shareholders or member producers. The Board of Directors of the Producer Company has to manage and operate the business. A Chief Executive of the company is appointed to provide a linkage in the Producer Company.

The same shall have the liability of its Members and can neither be limited by guarantee with or without share capital nor unlimited liability companies.
Functions of Board of directors of the Producer Company
The Board of Directors of the producer company is authorized to exercise the powers as mentioned in the article of the Companies Act. In order to maximize the benefits to the member producers, The Board of Directors of the Company undertake the following functions:


Rights of the Members of Producer Company
A member producer of the company is most important bit of the Producer Company. The company should ensure that the benefits are reached to the members of the company. The law has provided few rights to the members which each individual is allowed to exercise. The following are the rights of a member:
- to transfer his shares
- to vote on resolutions at meetings of the Company
- to requisition an extraordinary general meeting of the Company or to be a joint requisition
- to receive notice of a general meeting
- to attend and speak in a general meeting;
- to move amendments to resolutions proposed at meetings;
- in case the Member is a corporate body, to appoint a representative to attend and vote at general meetings on its behalf;
- to require the Company to circulate its resolutions;
- to enjoy the profits of the Company in the share of dividends;
- to elect directors and to participate in the management of the Company through them;
- to apply to the Company Law Board for relief in case of oppression;
- to apply to the Company Law Board for relief in case of mismanagement;
- to apply to the Court for winding up of the Company;
- to share in the surplus on winding up;
- to have a share certificate issued to him in respect of his shares.
Conclusion
Producer Companies as an Institution have been conceptualized and structured, taking into the considerations of farmers, agriculturists (termed as ‘Producers’), with a view that the business activities relating to agriculture, be channelized and governed in a formal manner.
At Registration Arena, we help register farmer producer company. Producer Company Registration in India can be done through Registration Arena in all major cities such as Hyderabad, Mumbai, and New Delhi, Chennai, Kolkata & all other cities in India.









